
Fish Vertebrates that Dominate Freshwater


Fish Objectives
-
Provide the characteristics of fish, including key structures used to distinguish fish from other living vertebrates.
-
Describe fish in hatcheries including life stages, feeding, and carrying capacity.
All tetrapods (mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians) are descendants of fish ancestors. Fish have brains in skulls, a spinal cord, and gills (human embryos still have gills too!). There are some characteristics we use to attempt to distinguish living fish from other vertebrate species.
Fish are a large group of vertebrate animals that share some similar characteristics.
This brief video introduces fish, the taxa (group) that gave rise to all vertebrates on Earth today.
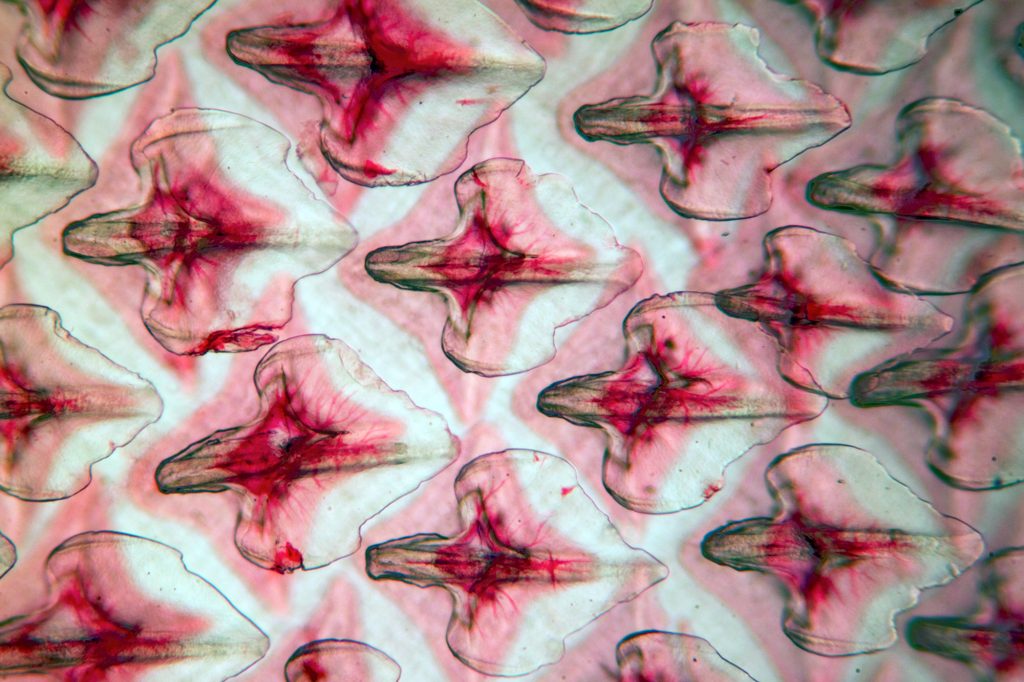
Scales are a significant integumentary structure in fish. The same genes that code for mammalian teeth and hair code for fish scales. Mutations have led to the the structural differences.
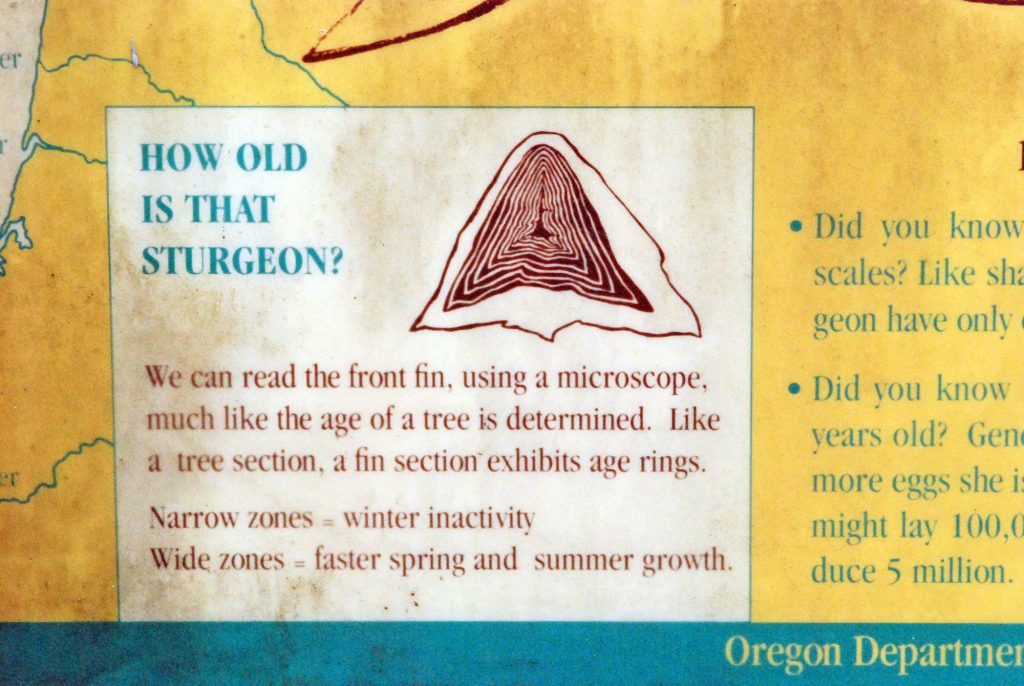
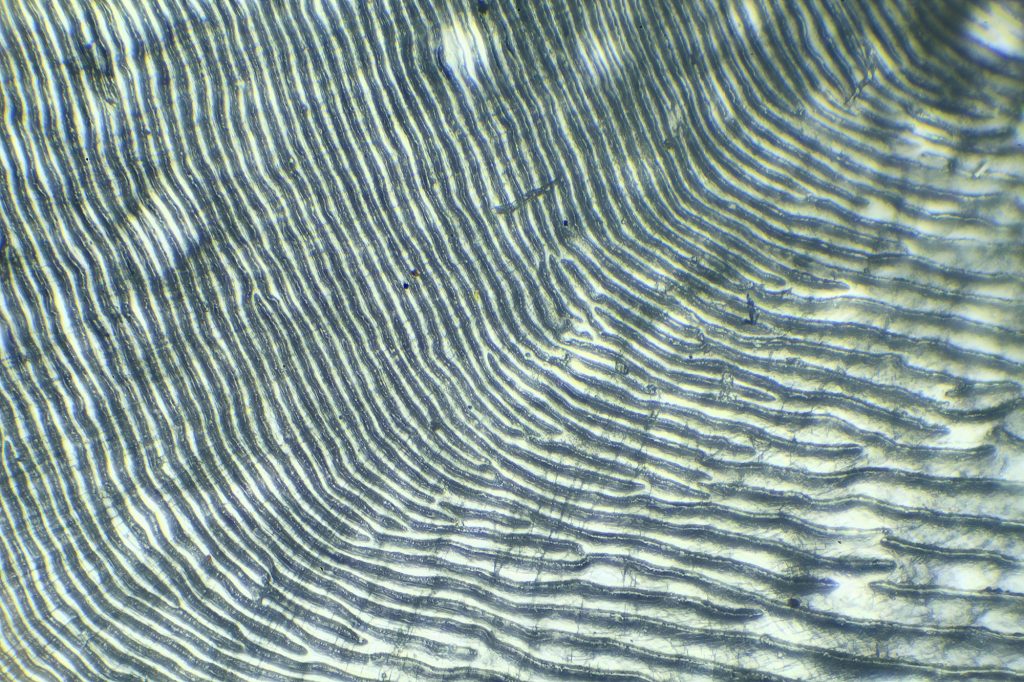
In some scales, layers indicate growth like the rings of a tree branch.
Starting our tour of fish at Cascadia Park on the Santiam River in Oregon.
Although we typically think of the adult life stage when we think of an animal, there are often far more immature individuals in a population; most may not survive until adulthood. These fish fry have recently hatched, but are attracting the attention of larger predators.
Next we are headed to a fish hatchery that raises rainbow trout.
Hatcheries typically have different rearing tanks with various life stages of fish. It is an opportunity to observe developmental changes.
As trout mature, gene expression changes, hormones are produced and we can obseve a phenotypic change in color.
For the trout to have reached this population size in a small pond, the carrying capacity must have been raised artificially. This includes supplying food and minimizing disease transmission.
It takes an enormous amount of food to raise fish in a hatchery. They are efficient eaters, all of these pellets will be consumed. Some will pass through the fish digestive tracts, some of the energy will be used to sustain respiration, and the remaining chemical energy may be stored, along with nutrients
This is the end of Guide 8B. Please proceed to the product page.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
provide the characteristics of fish, including key structures used to distinguish fish from other living vertebrates?
-
describe fish in hatcheries including life stages, feeding, and carrying capacity?



