
Hydrosphere Water Properties & Cycle


Hydrosphere Objectives:
-
Describe what a biogeochemical cycle is, providing examples of these nutrient cycles including sinks and the role of organisms.
- List key properties of the water molecule that make it significant for life as we know it.
- Describe ways water relates to the structures and distribution of plants.
Organisms, including humans, are comprised of the same basic nutrients, elements like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and more. Some of these elements have cycled through countless organisms and parts of the biosphere before they became part of our bodies.
We will start with a look at nutrient cycles, including the carbon cycle that is part of the greenhouse effect discussed in the previous atmosphere section.
Nutrients are basically elements, often cycling through organisms and the environment in simple molecular form.
Check how you are doing by answering these questions on the water cycle.
Here is a demonstration of transpiration you can repeat at home. You may even have more success if it is a bit warmer (faster evaporation/transpiration), or fresher plant material is utilized. Demos and at-home experiments can be used as evidence of course outcome achievement in the final portfolio. There are additional portfolio ideas on this guide’s resource page.
Setting up the demonstration.
Here are the results.
The water molecule has properties that make it conducive for life.
In chemistry courses, one of the first molecules you learn about is the water molecule. The orientation of the two hydrogen and single oxygen atoms results in a number of significant properties.
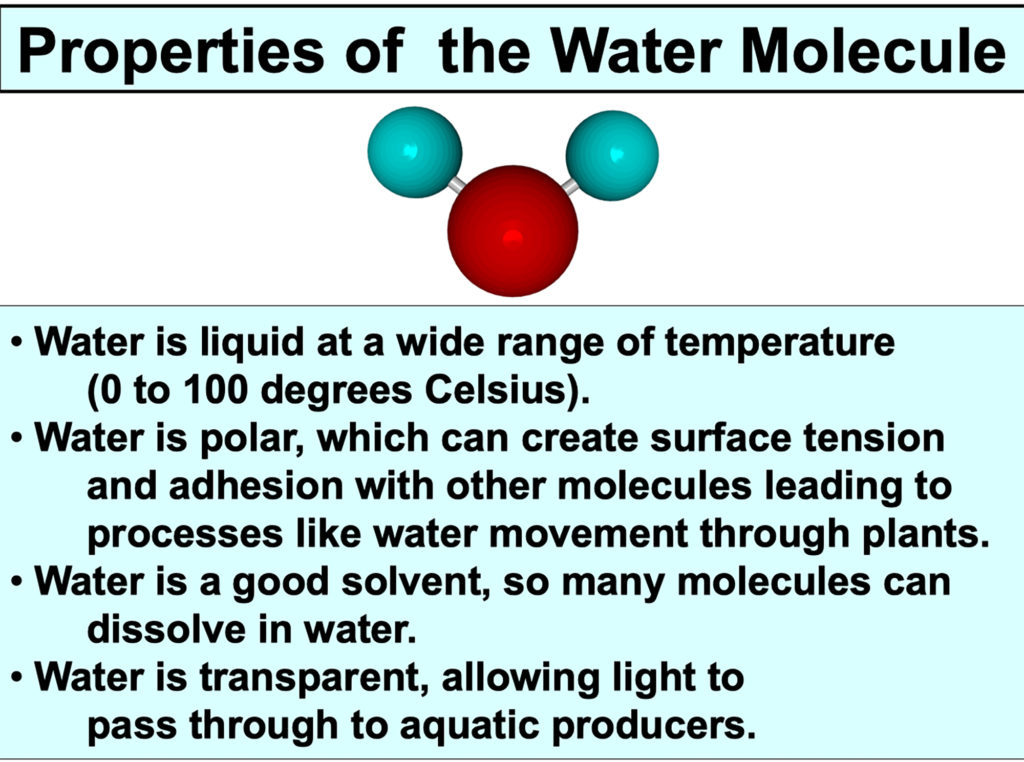
Water covers approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface and is found in all organisms. The molecule has a group of properties that make it well-suited for supporting life as we know it.
Water can also have a negative impact on organisms. Water indirectly impact plants by eroding away the soil.


Sometimes you can find a ribbon of trees within a larger grassland. That indicates water is present, possibly a stream or highway with ditches alongside.
Based on what you have just learned or your background knowledge, what is the answer to the question in this video?
Succulent (water storing) plants that live in desert habitats have a variety of structural features that reduce water loss.
We will take a closer look at succulent plants in Guide 3B.

The next section explores the lithosphere, including more detailed information on the nitrogen cycle.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
Describe what a biogeochemical cycle is, providing examples of these nutrient cycles including sinks and the role of organisms?
- List key properties of the water molecule that make it significant for life as we know it?
- Describe ways water relates to the structures and distribution of plants?



