
Decomposers All life goes here


Decomposers Objectives:
- Explain the role of decomposers in nutrient cycling.
- Define and provide examples of scavengers and detritivores.
- List the characteristics and functions of bacteria and fungi.
The same nutrients are used over and over, traveling through biogeochemical cycles, This section examines the role of decomposers in this process.
Compost
Composting is collecting organism waste materials, including yard leaves and kitchen scraps, and speeding of decomposition, with the intent of recycling nutrients back into the soil.
The decomposition process relies in large part on organisms that break down dead organisms, or parts of organisms.
Soil Organisms
This video introduces organisms that often get overlooked because they are small and do much of their work out of sight in the soil.
Many organisms depend on other organisms that have already died.

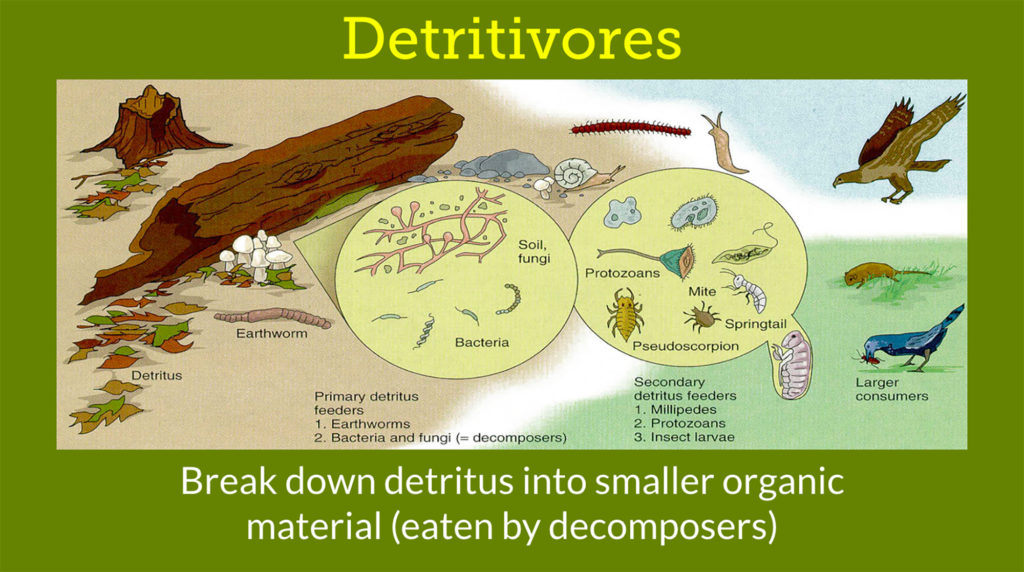
Scavengers break down a recently dead organism (a corpse) into smaller pieces called detritus.
Detritivores eat small recently dead organisms and pieces of detritus from larger organisms.

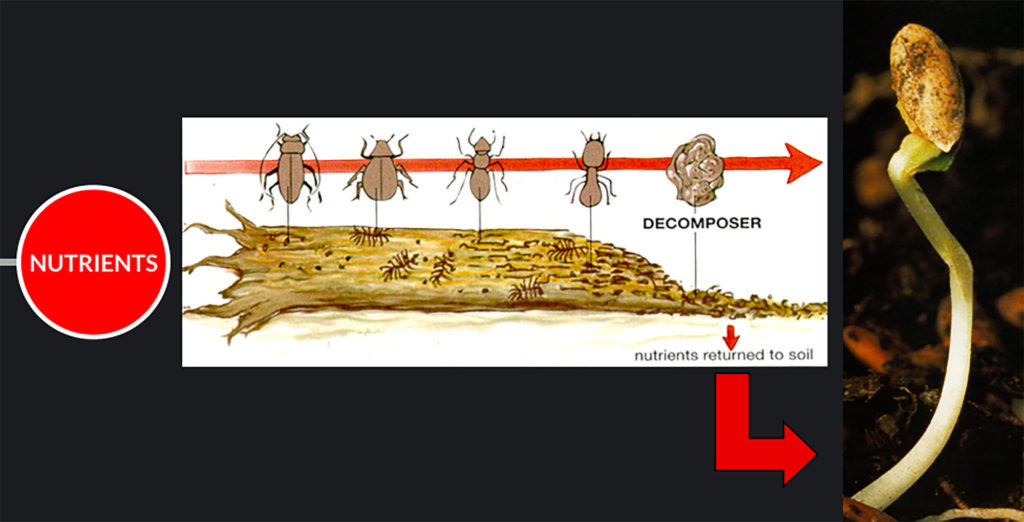
Decomposers, including fungi and some species of bacteria, break organic matter into small molecular form, enabling nutrients to recycle back to the producers.
Fungi & Bacteria
One of the smells of autumn in the Willamette Valley is decomposing mint compost, chopped up stems from mint fields. This pile already has white hair-like structures and mushrooms indicting that decomposition in underway.
In the early morning, steam can be seen rising from the compost pile. What process is being carried out by the fungi and bacteria decomposers that is generating this heat?
This video provides an overview of the fungi and bacterial decomposers.
Fungi can play a key role in decomposition within soil food webs. From the video, answer these questions.



Bacteria are significantly different that fungi, but some species of bacteria are also decomposers.



Morel mushrooms are a delicacy, but any mushroom hunter knows that this species and many others require specific microhabitats. For some reason, these appeared right next to a gravel path.
Always use care and expertise when identifying a mushroom prior to consumption. Toxic species have spread into many areas.
Fungi reproduce with spores, but they are too small to see without a microscope. Spore prints can reveal differences.
Some fungi are fully microscopic and other have reproductive structures that do not resemble mushrooms. These cup fungi have spores in bowl-shaped structures. The spores splash out when struck by a drop of water.
This is the end of the Food Web Guide. Material from this guide and the Animals Guide will be assessed on the quiz due by Sunday.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- Explain the role of decomposers in nutrient cycling?
- Define and provide examples of scavengers and detritivores?
- List the characteristics and functions of bacteria and fungi?














