Fruits & Seeds Laboratory & Media Piece


Fruits & Seeds Objectives:
Describe and explain the structures, functions, processes, and classification of fruits and seeds critical to humans.
In addition to the videos provided below, background material for this lab can be found in last week’s Food Webs Guide.
For quick reference, click each link:
Media Piece Assignment
Fruits & Seeds
For this piece you are making media that describes and explains aspects of fruits and seeds in relationship to human consumption. Your media (photos, sketches, captions, creative writing, video, etc.) will include each of the following:
-
How flowers become fruits and seeds.
-
The basic structure of a monocot seed and a dicot seed.
-
The basic process of seed germination.
-
Two examples of commercially significant seeds.
-
Two different ways that fruits and seeds can be dispersed from their parent plant.
-
Classification of two different fruits.
-
An example of an economically important fruit in the Pacific Northwest.
This media piece can populate the Science Connections portion of the final portfolio. Fruits and seeds are critical in the human diet, and successful crop production relies in part on the agricultural sciences.

You are submitting to Canvas
A media piece of your original work (photos, captions, creative writing, sketches, etc.) that provides information on fruits and seeds in the human diet. Include: how flowers become fruits and seeds; the basic structure of a monocot seed and a dicot seed; the basic process of seed germination; two examples of commercially significant seeds; two different ways that fruits and seeds can be dispersed from their parent plant; classification of two different fruits; and an example of an economically important fruit in the Pacific Northwest.
Work Ahead
If you run across fruits on plants around campus or as part of a meal, you can include photos in your assignment.
You are welcome to use the material on this page to develop your Fruits & Seeds media piece.
Flowers to Seeds
In the human diet, seeds are a significant source of energy and nutrients. On this page, we are linking seeds to the basic flower structure we have already covered. In the next section, we will examine seed structure, followed by the structures and functions of fruits.
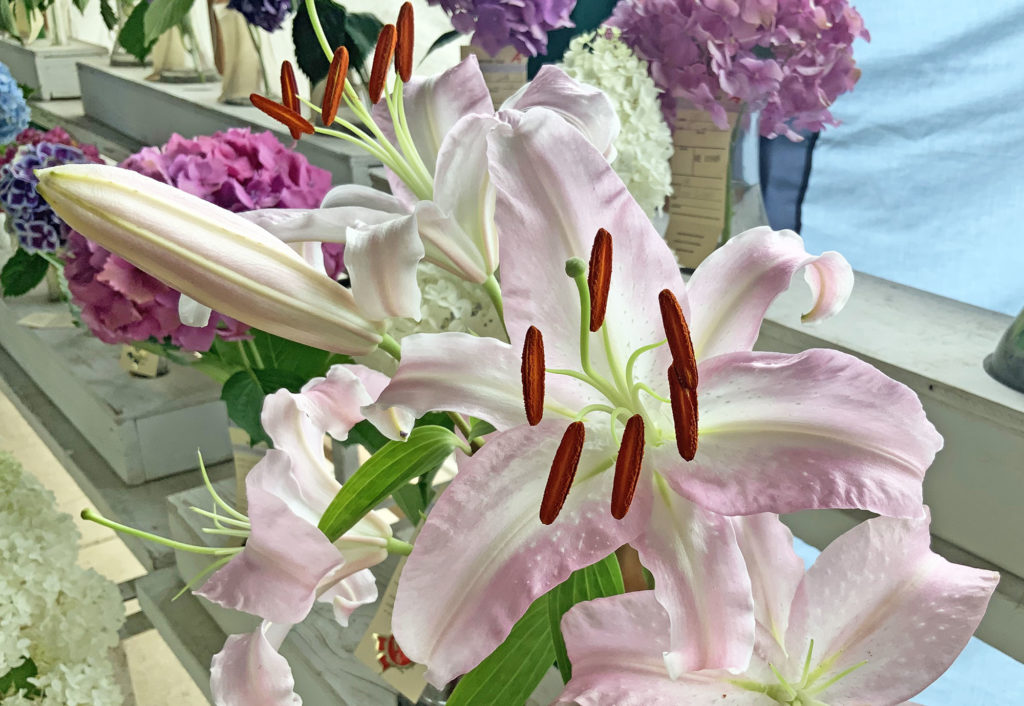

A quick review of flowers:
Can you identify the stamen (pollen on the anther, attached to a long filament) and the stigma the pollen would land on with the style that carries the pollen down to the ovary?
Now we are focusing on what is produced after flowers are pollinated: fruit and seeds.
Since fruits may mature weeks or months after flowering, many people do not visualize the flower that produces a fruit. Tomato plants, like the roses can simultaneously display both flowers and developing fruit.
These are the general signals of seasonal changes far from the equator: spring is for flowers, summer is for developing fruit, and autumn is for harvest. You can predict the season when we made this video.

Many of the foods we eat are dependent on flowers and pollination of flowers to produce seeds and fruit.
The next section details the significance of seeds in the human diet.
Fruit Structure and Function
From your own background knowledge; fruit develop from plants that have _____. What are the primary functions of fruit? _______
Answers: flowers; protect & disperse seeds

A fruit is a ripened (mature) ovary that protects and may disperse seeds. When the fruit ripens, it can be fleshy (moist) or dry.
There are two general categories of fleshy fruits (complex or simple) and two general categories of dry fruit (ones that rupture or others that don’t).
Fleshy Fruits – Simple
This video provides an overview of fleshy fruits.
Fleshy Fruits – Simple
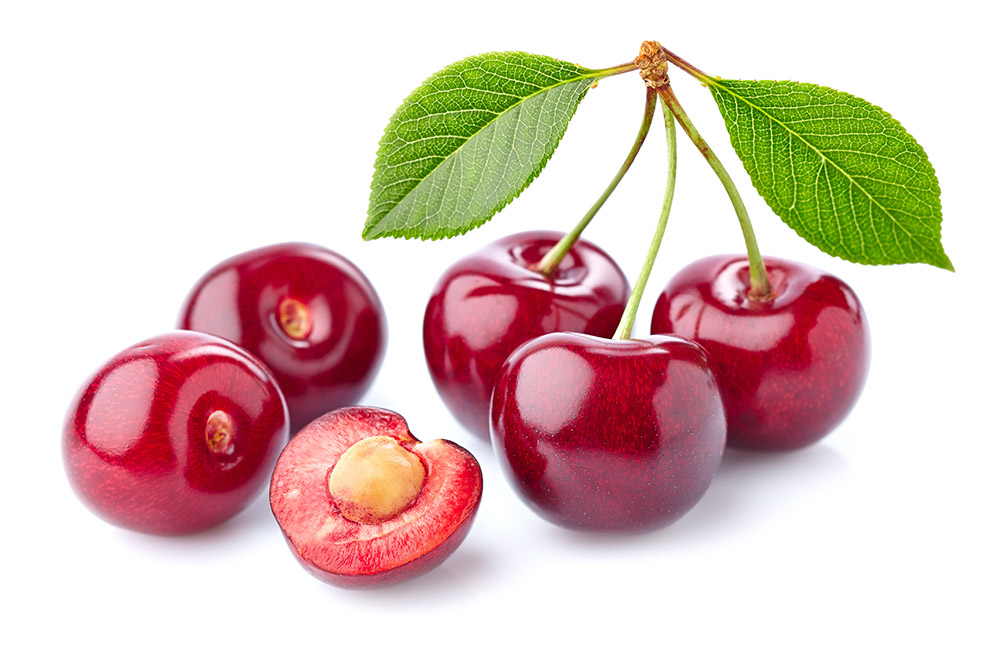

Drupe
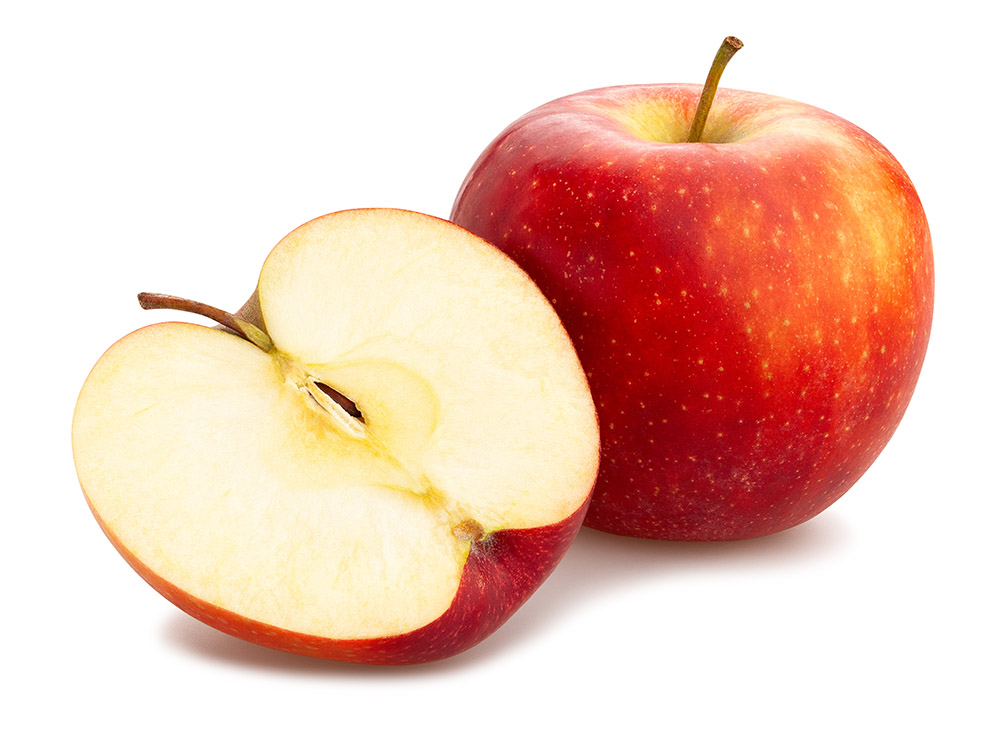

Pome
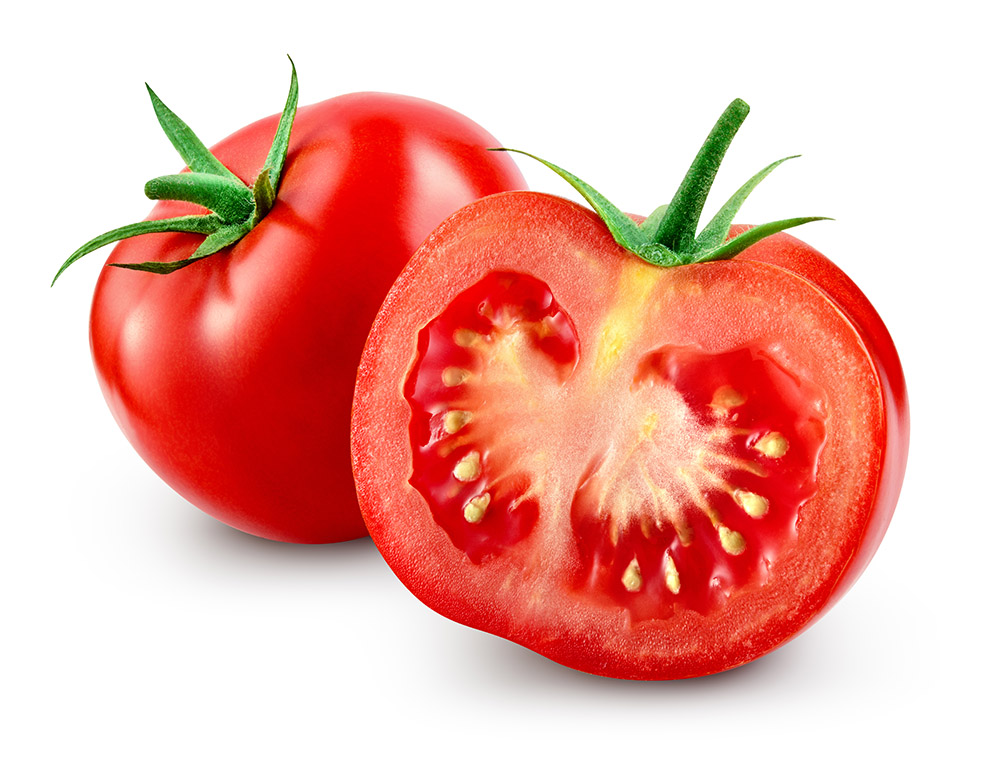

Berry
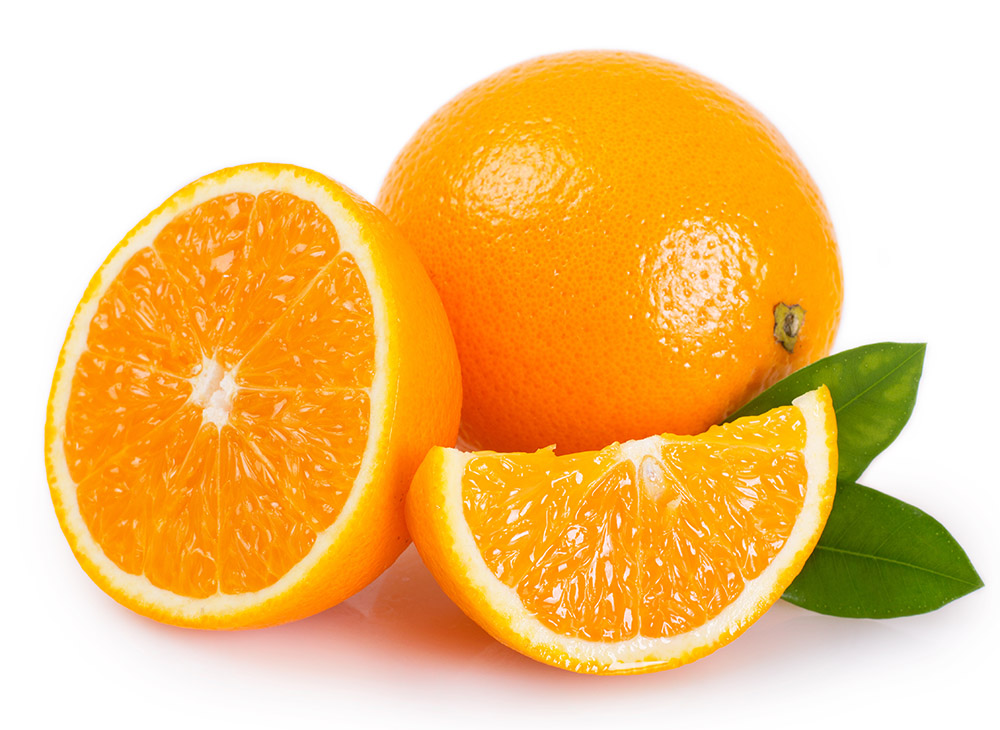

Hesperidium
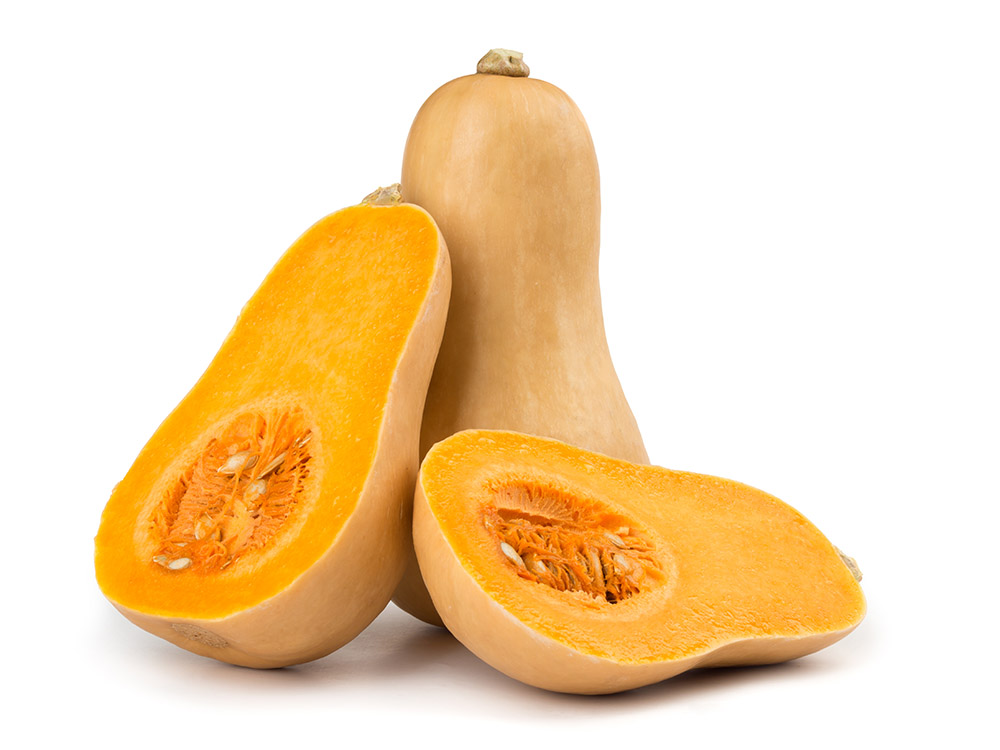

Pepo
Different fruit structures can relate to the primary roles of a fruit: to protect and disperse the seeds.
Fleshy Fruits – Complex
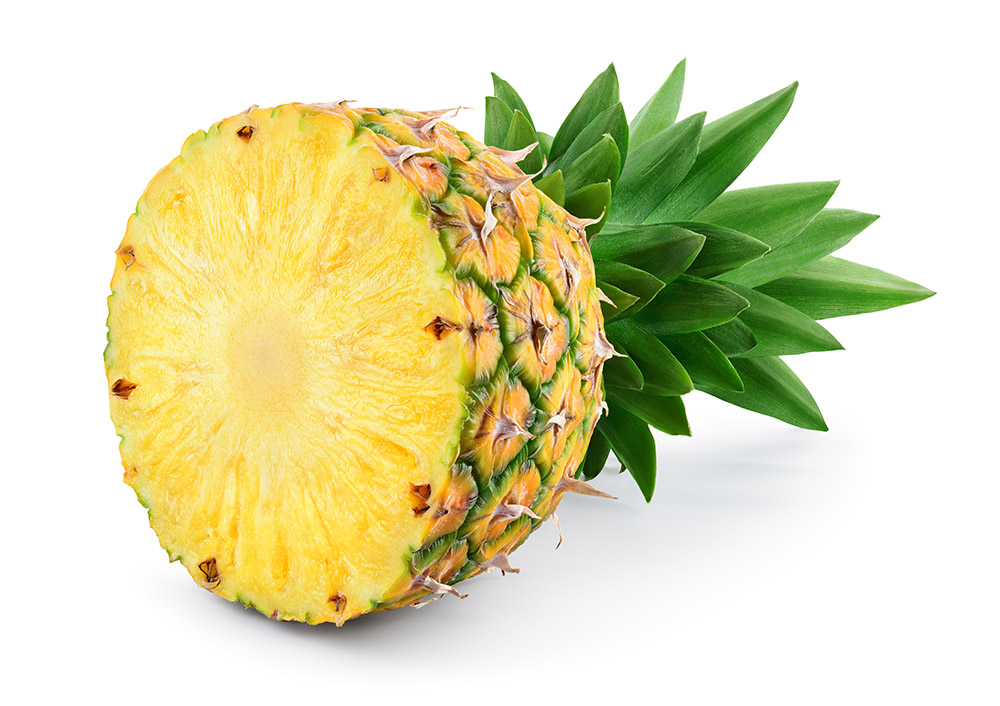

Multiple Fruits
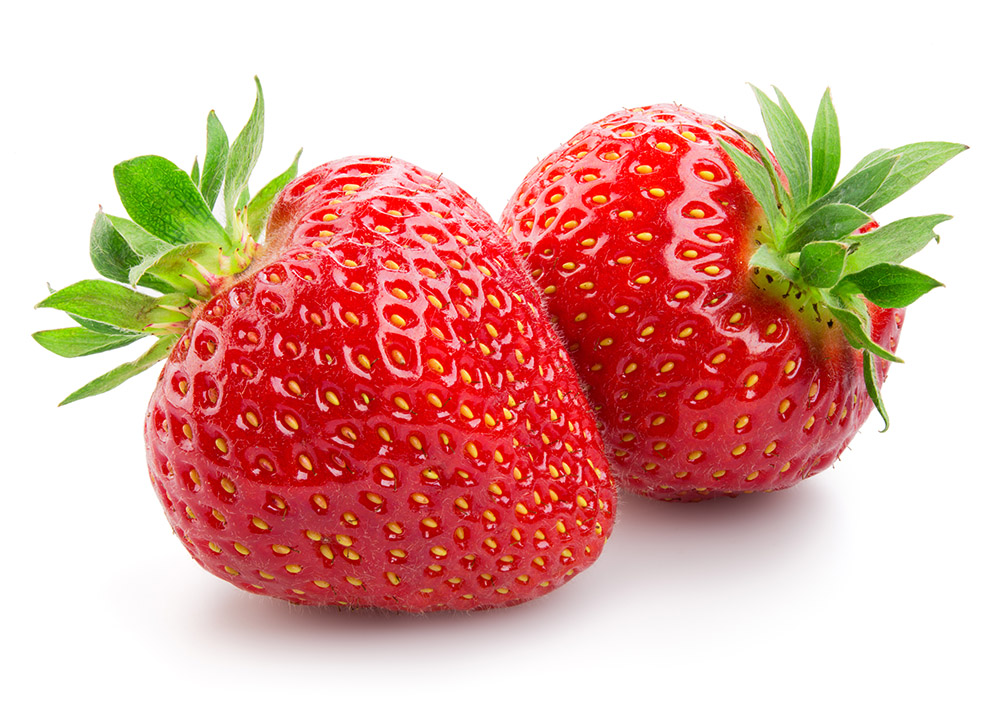

Aggregate Fruits
Are peppers fruits or vegetables?
Find out here.
Dry Fruits
This video provides an overview of dry fruits.
Dry Fruits – that do not rupture open
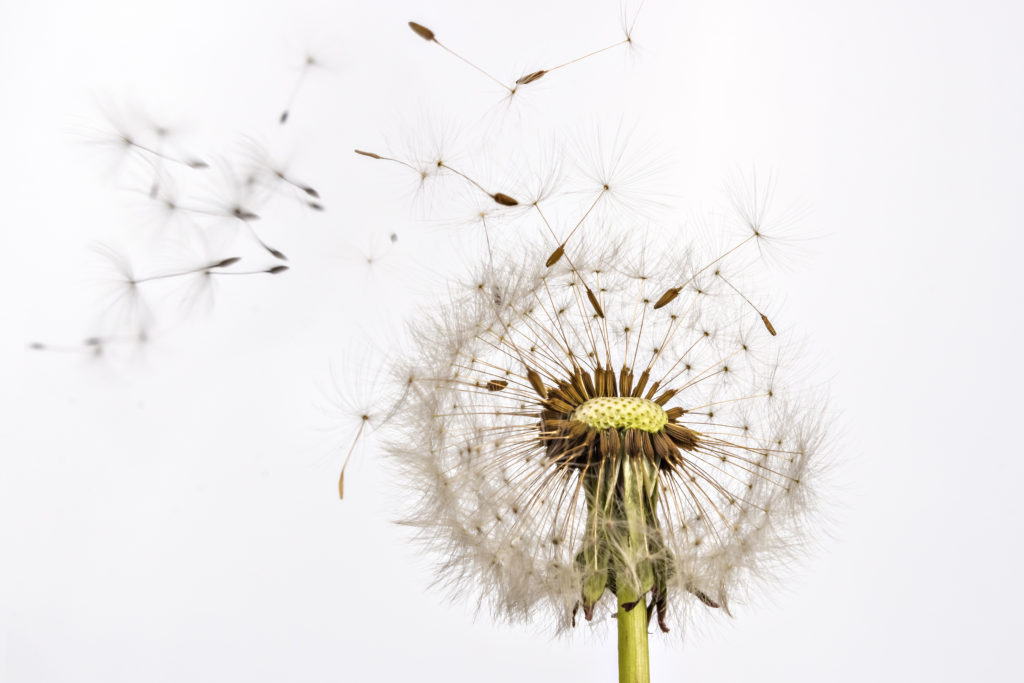

Achene

Samara
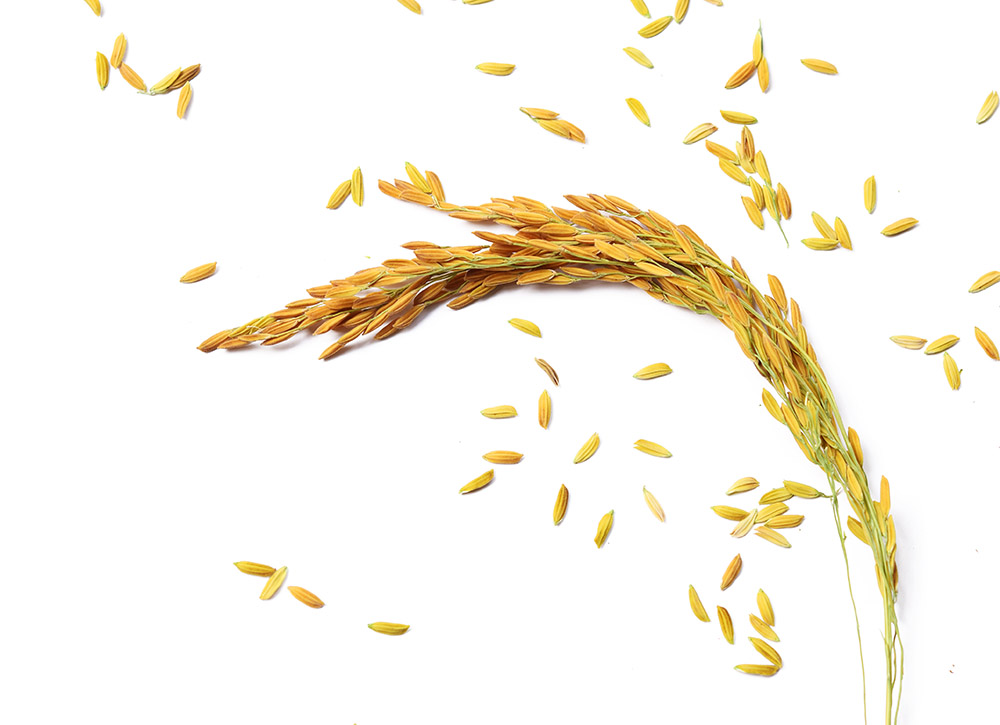

Caryopsis
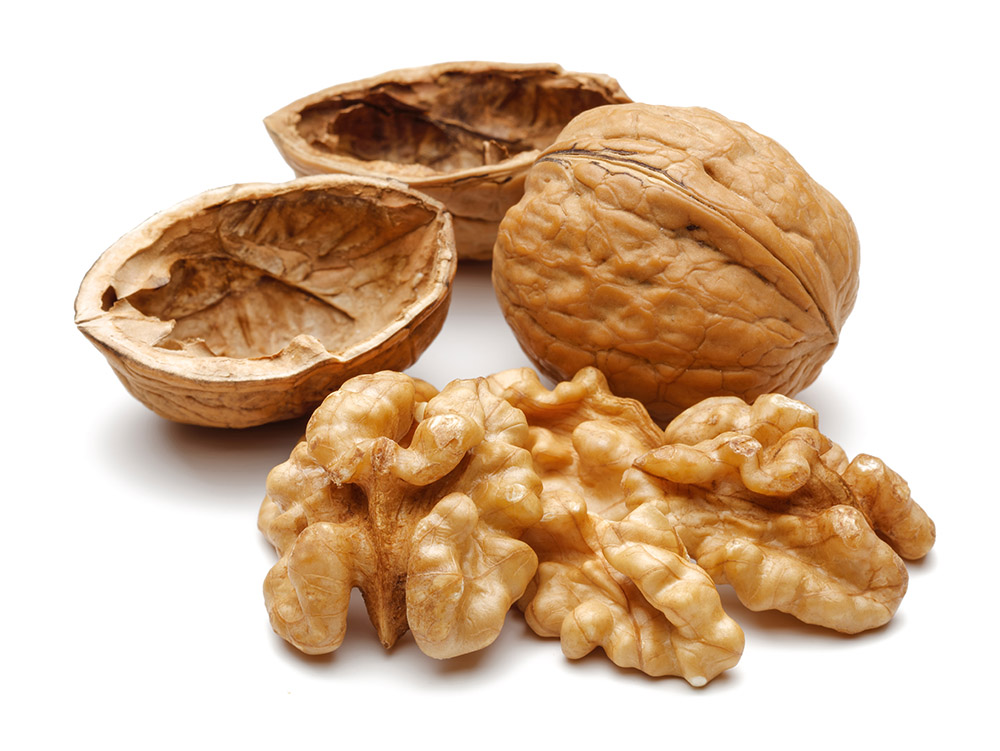

Nut
Dry Fruits – that rupture open

Capsule
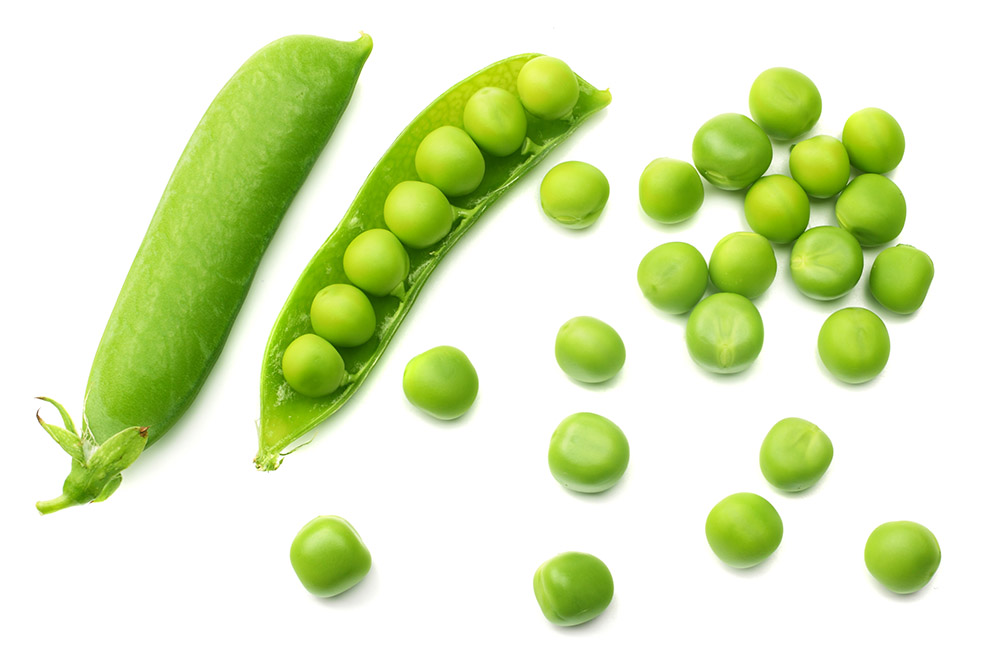

Legume
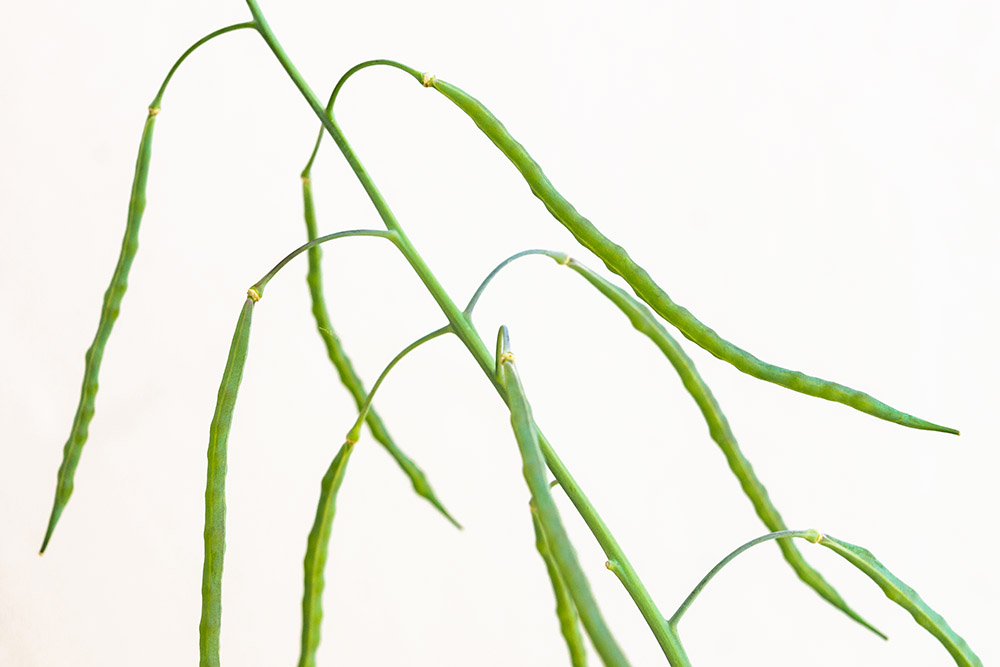

Silique
Check your knowledge: which of these are fleshy fruits and which are dry?
Dry fruits in the video are: nut, samara, achene, silicle, legume, capsule, caryopsis
Check your knowledge! Can you identify these fruit types?