
Population Data Looking Within a Species


Population Data Objectives
- Define what a population is and provide examples.
- Read a population size chart, including identifying carrying capacity and providing examples of factors that can limit a population’s carrying capacity.
- Analyze different forms of population data including population distribution.
There is a limit to the number of individuals that can live in a population
What can limit population size?
This video has the answers.

Sea star wasting is caused by a pathogen and rapid loss of sea star species had a significant impact on the tide pool community of species on the west coast of the United States.
We have all heard of “starfish” sea stars. Why would their loss impact other species? Think about the possible functional roles they can play.

A hint is that sea stars can use their legs that are covered in tube-like feet to pry open clams and other tide pool mollusks.
Sea stars eat a variety of prey species, and the loss of sea stars means the population controls on clams, snail, and other species are reduced. Clams grow in population size, causing a decline in what they consume. There is a cascade of impact with the loss of the sea star predator.
Some people consider sea stars to be a keystone species, meaning that they may not have a large population biomass, but the presence (or loss) has a large impact on other species.

In the Willamette Valley, a sign of fall is the return of Dusky Canada Geese populations from their summer breeding grounds in Alaska. We’ll have more on the geese in an upcoming guide.
Dusky Canada Geese
Madagascar Hissing Cockroaches (Gromphadorhina portentosa) are a popular pet. However, if you overfeed them their populations size can quickly grow because you have raised their ________________.
hint: this is “K” in the video.
Besides size, another characteristic of populations is distribution of the organisms.
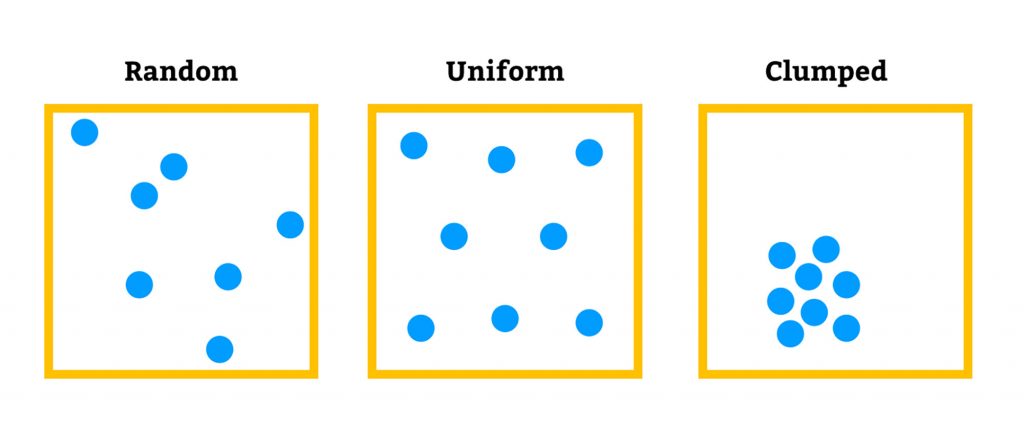
The blue dots in the image represent individuals in a population.
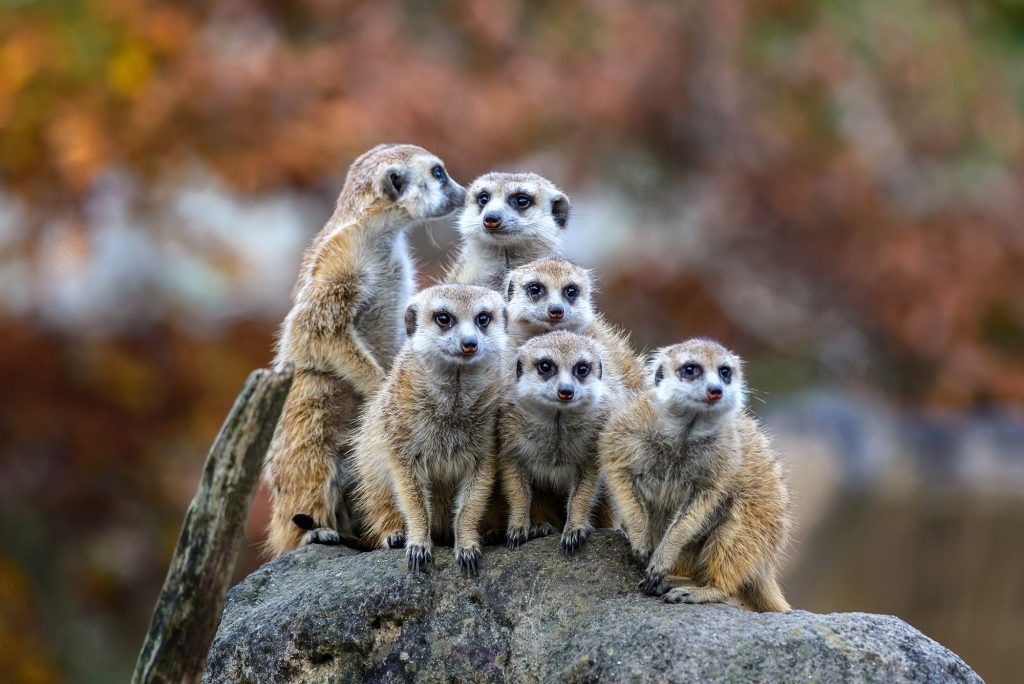
The meerkats in this photo are demonstrating _____ distribution.
answer: very clumped

Another form of population data is the type of interaction between organisms, either within a species or between species.
Commonly observed interactions
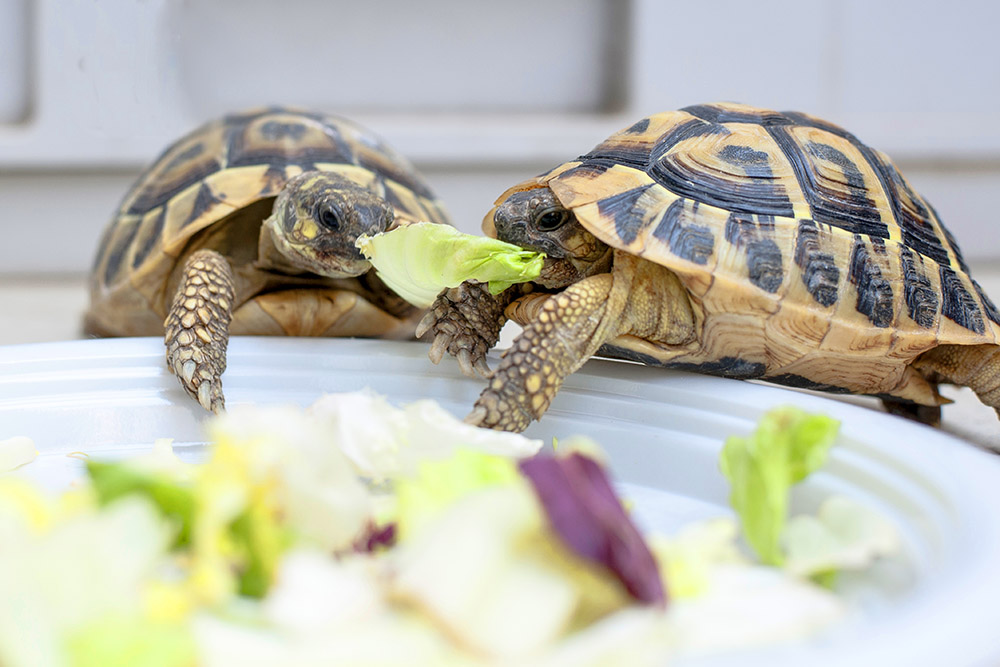

Competition
organisms try to utilize the same limited resources
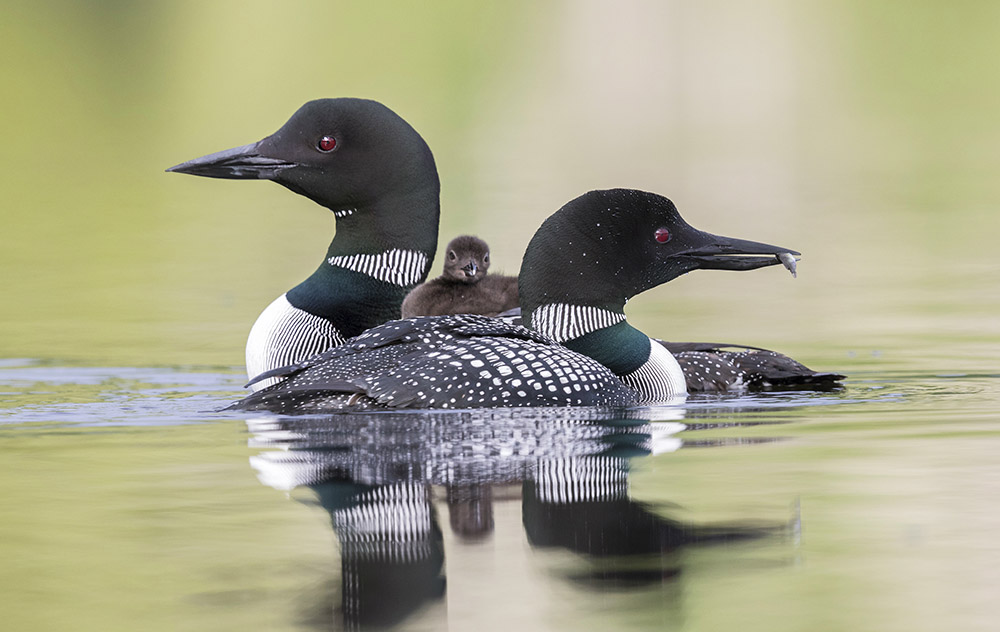

Cooperation
Organisms benefit each other in some manner
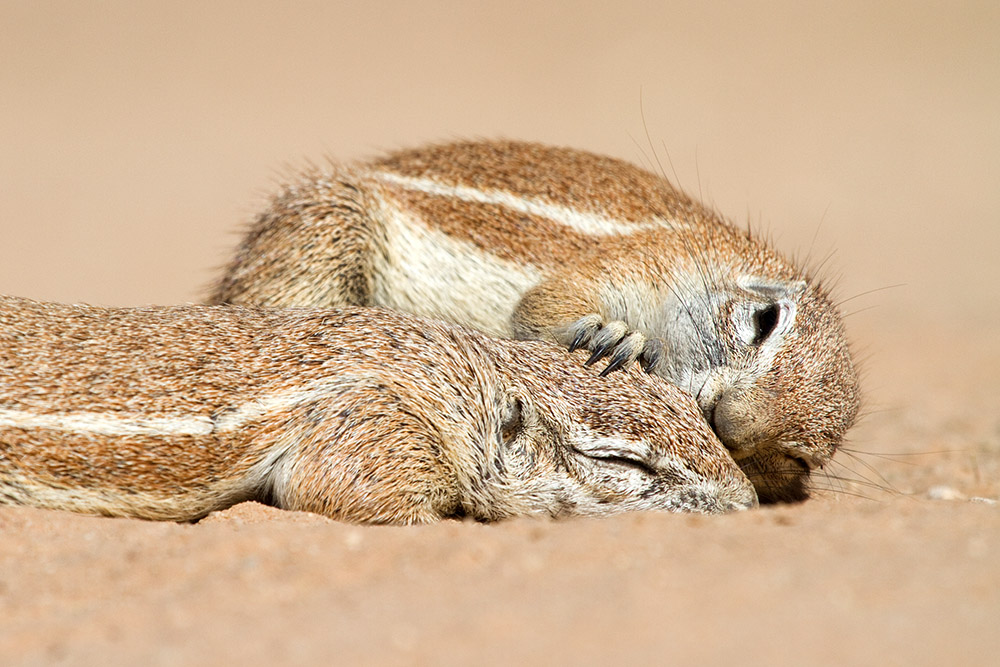

Altruism
An organism is harmed assisting another organism
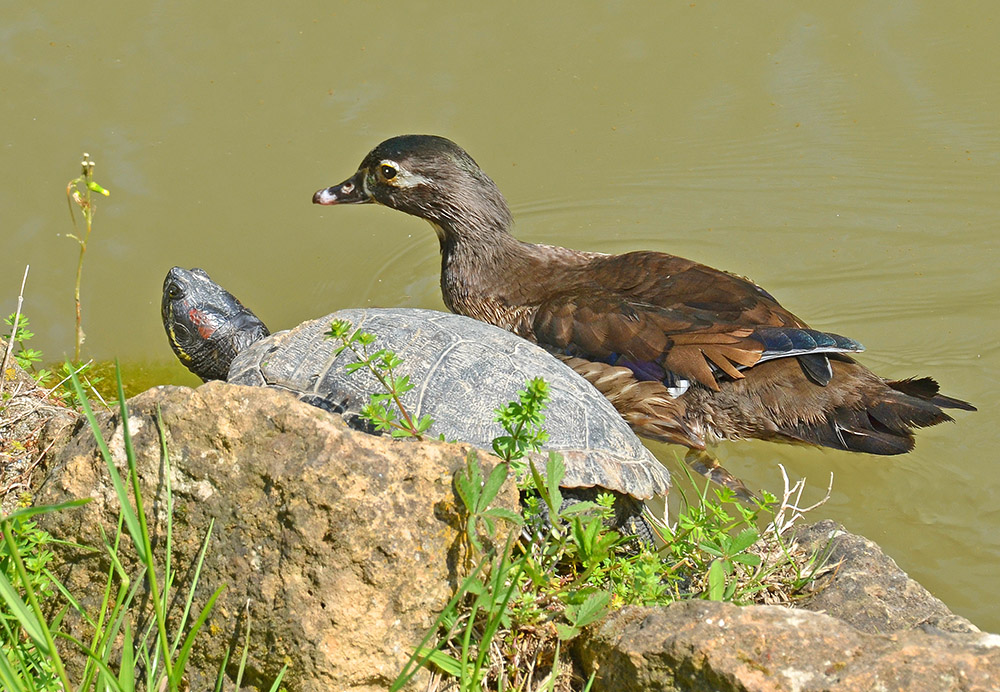

Undetermined
Many interactions are difficult to study and/or characterize
Organisms within a population can end up competing for limited resources. The next section introduces animal competition.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- define what a population is and provide examples?
- read a population size chart, including identifying carrying capacity and providing examples of factors that can limit a population’s carrying capacity?
- analyze different forms of population data including population distribution?



