
GMOs Genetically Modified Organisms


GMOs Objectives
-
Describe what gene editing is, where the process originated, and the impact of precise DNA manipulation.
-
List the types of genetically modified organisms that have been produced, the techniques used, and rationales.
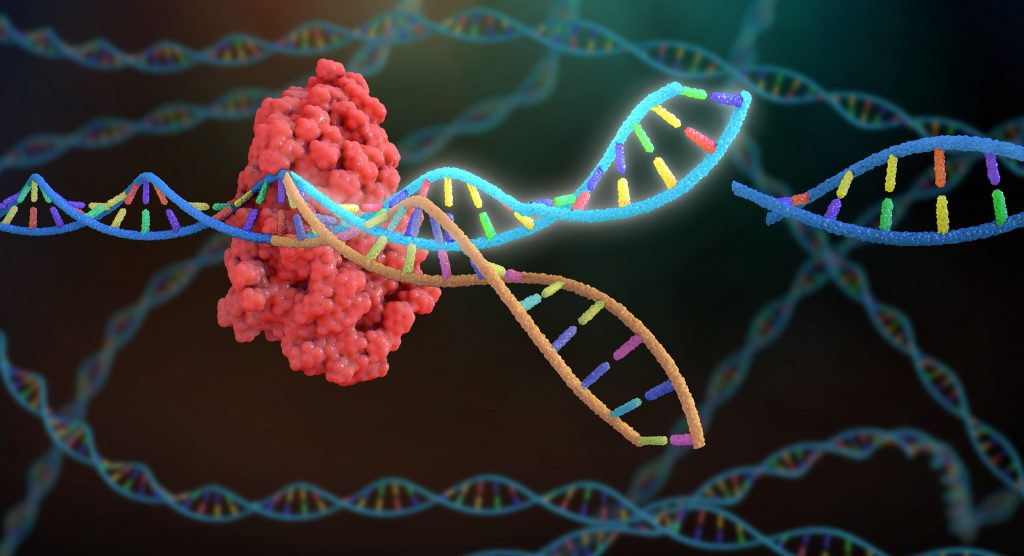
There are many genetic engineering techniques as introduced in the previous section, but now “gene editing” has a more specific meaning.
Bacteria have a sophisticated defense system against bacteria that involves genetic manipulation, and researchers are harnessing and altering their system to create engineered nucleases including CRISPR-Cas9.

This video introduces where CRISPR came from and how it is used.
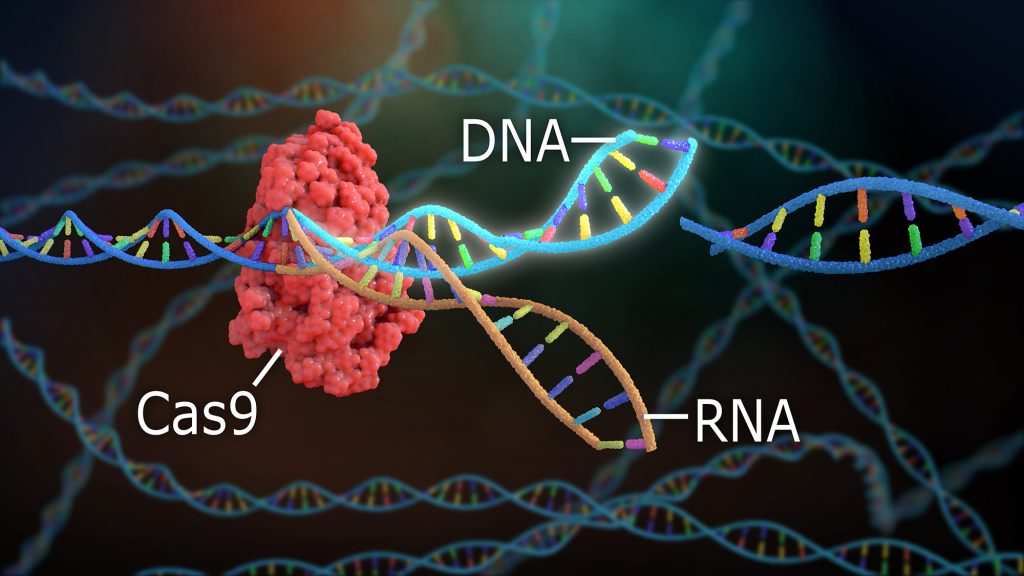
Researchers can use specific guide RNA to direct where CRISPR-Cas9 cuts the DNA. This enables precise deletion of a gene, or cutting open DNA to insert a new gene.
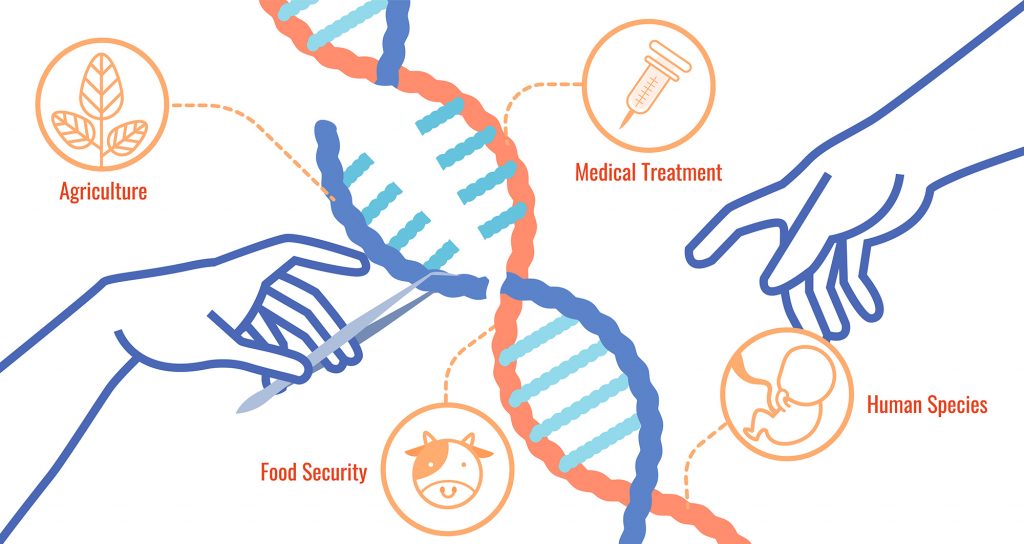
There are numerous potential applications of gene editing, and this technology is getting ahead of the debate and legislation that will likely regulate uses of these techniques.
In module #10 you will have an opportunity to write an opinion piece over a course topic of your course, and it could be your thoughts on using genetic technologies like gene editing.
GMOs
Genetic technologies, including gene editing, are being used to modify a variety of organisms. Typically GMOs are created to solve significant medical and food supply issues. However, as the GMOs video will show, some GMOs are produced for other uses, including the pet trade.
An introduction to GMOs, including engineered animals.
An indicator of how established genetic engineering is becoming is the presence of GMOs in pet stores, including several transgenic fish species. “GloFish” is a trademarked name. GMOs can be patented and their sales restricted.
These are our “Glofish” transgenic danios that contain jellyfish (or coral) genes that enable them to glow bright colors. When you cross them, the resulting offspring are a mix of the two parental colors. For example, a red parent and a yellow parent produce orange offspring. This is not the old “blending theory,” this is co-dominance, both alleles direct the production of a large amount of pigment.
Engineering species like trout may produce larger fish faster, or fish that tolerate a wider range of hatchery and environmental conditions.
A lingering question about GMOs is whether they should be released into the wild, with potential for gene flow with both wild and artificially selected species.
The next section provides an overview of fish, including their shared structures.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
describe what gene editing is, where the process originated, and the impact of precise DNA manipulation?
-
list the types of genetically modified organisms that have been produced, the techniques used, and rationales?



