
Animal Defenses Flight, Fight, Freeze, and More


Animal Defenses Objectives
-
List different types of animal structural and behavioral defenses and provide an example of a species that utilizes each defense.
-
Describe different forms of camouflage including the species and form of camouflage, and how the camouflage works.
Prey animals are not just waiting to be eaten; they have a variety of defenses that enable them to elude predation.

Species that are vulnerable to predation have a combination of structures and accompanying behaviors to escape being eaten.
This video demonstrates a variety of prey defenses.
This “feigning beetle,” native to southwestern North America, has a response that is similar to opossums. Watch its response to being picked up and how quickly it recovers.
Sea slugs like terrestrial slugs are mollusks, relatives of snails, clams, and octopuses. Most seas slugs can release potentially toxic substances when attacked by a potential predator.
In some cases, prey are defending family members. This kildeer doesn’t actually have a broken wing, it is flapping an uninjured wing while loudly squawking to draw attention away from its nest, full of eggs. Once the predator closes in, it will fly out of reach. The kildeer is in danger of being eaten itself, but if its offspring survive, it will pass on its genetic information.

Camouflage
Camouflage sounds simple: blending in with your surroundings. However there are diverse forms of camouflage that address particular threats.
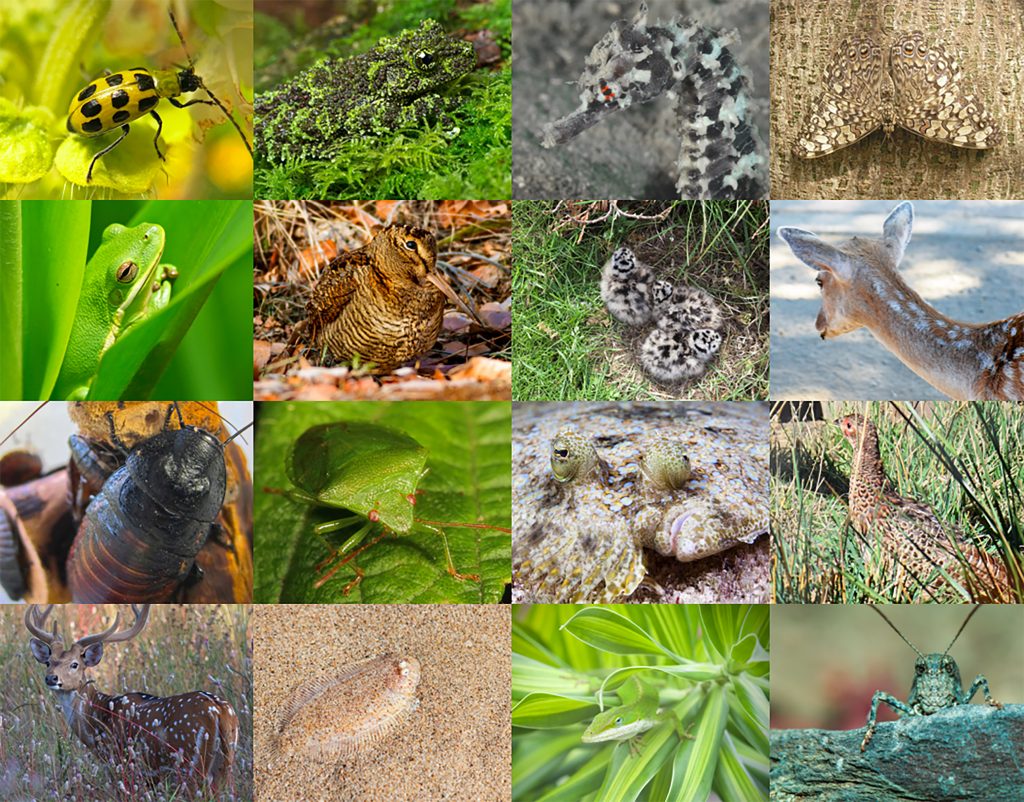

Patterns mimicking shade and dappled light enable even large organisms to blend into their surroundings.
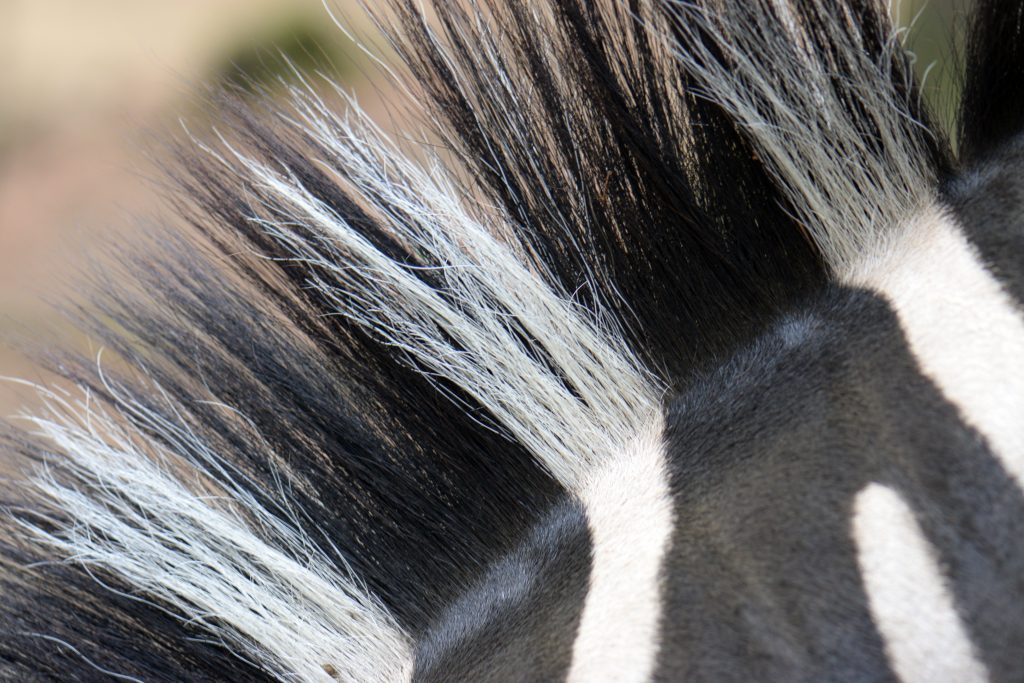
Vertical striping can enable herbivores to blend into grass fields, or make it difficult to discern between individuals in a herd.

Vertical striping patterns enable these fish to blend with aquatic plants and algae.
Iridescence in fish and insects may make it difficult for predators to follow prey as they move from light to shadow.
Countershading, different colors on the top and bottom of an animal, allows it to blend with sky from one angle, and ground or water from the other.
Note how color, pattern, and reduced movement work together to camouflage these species.
Some insect species flash a bright color when they are approached by a predator. This may temporarily startle the predator, enabling the insect to escape. These are two different moth species that “flash and startle.”

Moth adults and larvae (caterpillars have a variety of forms of camouflage. This video introduces “eye spots.”
A photo of eyespots on a butterflyfish and the Io moth.

Taking it a step further, these caterpillars have abdomens that look like false snake heads. They can even inflate them to look more menacing.

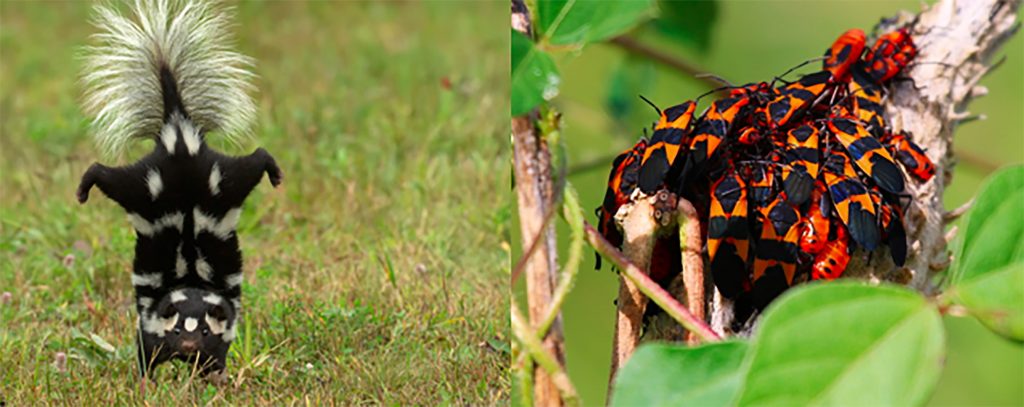
Some species, including this skunk and milkweed bugs use bold colors to warn away potential predators. Bright colors can indicate chemical toxins are present.


Another option is to mimic something a predator is not likely to eat. This hoverfly looks like a bee, and is less likely to be eaten by birds. If this hoverfly survives and reproduces, it has a high level of fitness due to its appearance.
The species on the left is unpalatable and unlikely to be eaten by birds. The species on the right is a mimic: it looks similar enough to the other species, birds will not eat this one either.


Humans have adopted the idea of mimicry to develop new materials and services.
Biomimicry is designing products that are based on structures found in nature.
Understanding how animal structures relate to their functions has led to the development of human products, a clear connection between science and other fields of study.
This is the end of the Nutrients Guide. Material from this guide and corresponding lecture, along with the next Predation Guide are assessed on the weekly quiz.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
-
list different types of animal structural and behavioral defenses and provide an example of a species that utilizes each defense?
-
describe different forms of camouflage including the species and form of camouflage, and how the camouflage works?



