
Functional Groups Producers, Consumers, & Decomposers


Functional Groups Objectives:
- Describe the ecosystem roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers.
- Provide examples of organisms representing different functional groups.
Organisms can be classified based on their structures and/or based on the role they play within an ecosystem. We previous met taxonomic classification; this page describes functional classification.

Taxonomic Classification
This is the classification system based on structures and evolutionary relatedness.

Functional Classification
This is the role an organism plays in the ecosystem, including how it relates to other species.

An Oregon White oak tree (Quercus garryana) is taxonomically classified in Domain Eukaryota, Kingdom Plantae, Phylum Angiosperm, Class (Clade) Dicot, Order Rosids, Family Fagaceae, Genus Quercus and species garryana.
Its functional classification is producer.
Functional Groups
Now that we have some of the vocabulary, this video reviews these terms and provides an overview of food web concepts found throughout this guide.
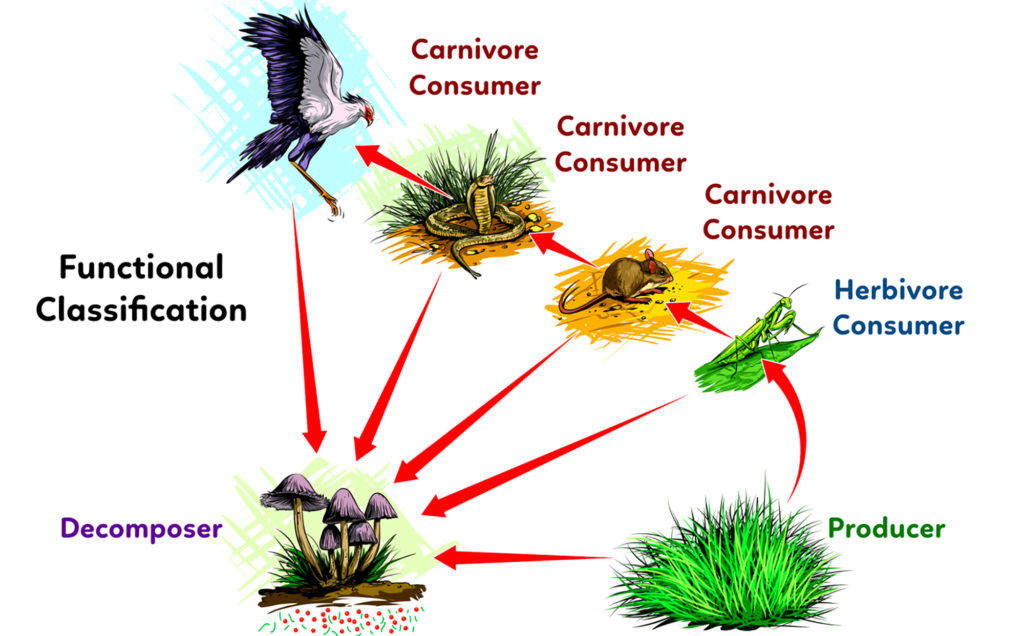
Animals need to consume other consumers for nutrients and energy:
Herbivore consumers eat ___.
___ consumers eat other consumers, or their recently dead remains (scavengers)
___ can eat producers and consumers
Animals do not choose their functional group, they have digestive organs, feeding structures, dietary requirements, and behaviors that obligate them to eat certain foods. This jumping spider only eats other consumers, classifying it as an obligate carnivore.

Of the different consumer functional groups, which has the most potential flexibility in diet?
Answer: omnivores like humans, foxes and crows can live off different foods in a variety of habitats
This video uses a poster to review the basic functional groups.
The next section explores why there is typically far more producer biomass than consumer biomass in an ecosystem and introduces seeds.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- Describe the ecosystem roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers?
- Provide examples of organisms representing different functional groups?



