
Patterns Searching for Repetitive Occurrences


Patterns Objectives:
- Describe what a pattern is and provide examples of patterns in nature.
- Identify different forms of population data including a population size chart, carrying capacity, and population distribution.
- Provide the names, locations, and characteristics of temperate grasslands.

Patterns are repetitive occurrences that are used to identify and classify.
Humans are continually searching for patterns and using identified patterns to make sense of the natural world. One of the characteristics of our amazing brains is strong pattern recognition.
This video describes how important pattern recognition is in studying nature.
Populations
Pattern recognition is important in studying populations of organisms.

From the Course Topics page, a population is a group of interacting members of the same s_____.

A population is a single species of interacting organisms. For example, we are all part of the population of Homo sapiens.
The ants in this photo are the same species and their population is building a physical bridge across two leaves.
Populations of organisms have a maximum size due to limited carrying capacity, the number of individuals a habitat can support.

Carrying capacity is limited by the amount of food, space or other resources. Adding extra food to this container has led to a population explosion of mealworm beetles (eggs, larvae, pupae, and adults).
If you would like to start your own mealworm beetle colony (the larva are often used to feed pet reptiles), there is a how-to video on the resource page.
Madagascar Hissing Cockroaches (Gromphadorhina portentosa) are a popular pet. However, if you overfeed them their populations size can quickly grow because you have raised their ________________.
hint: this is “K” in the video.
Besides size, another characteristic of populations is distribution of the organisms.
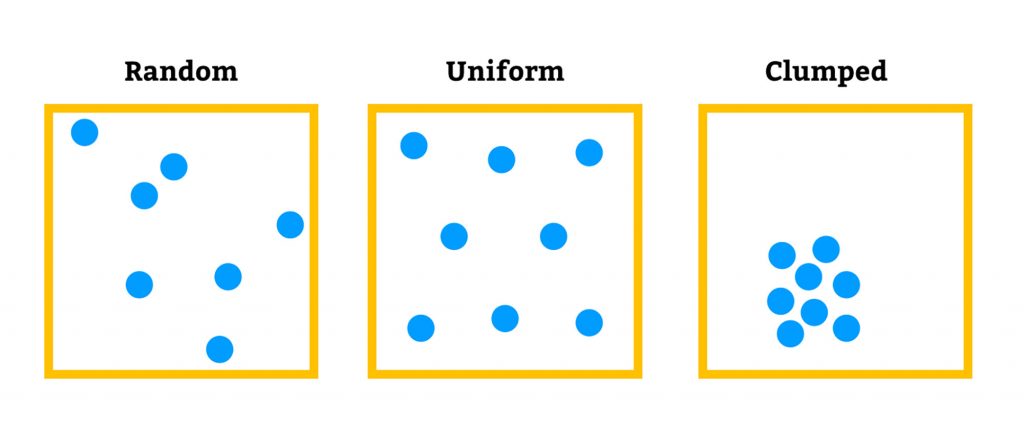
The blue dots in the image represent individuals in a population.
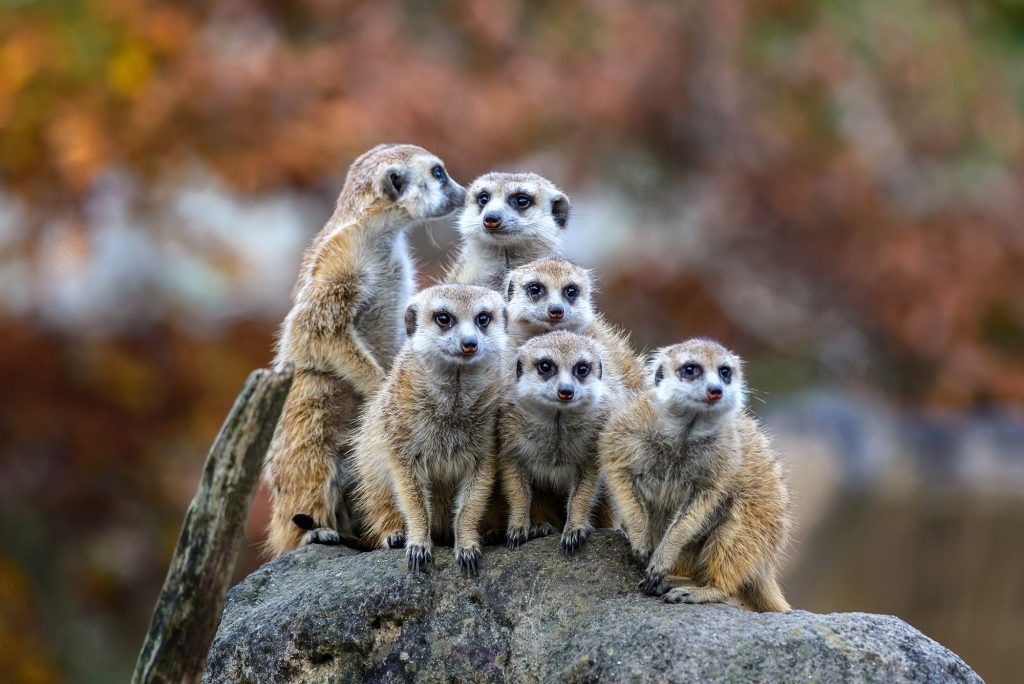
The meerkats in this photo are demonstrating _____ distribution.
answer: tightly clumped

Temperate Grasslands
Many people live in a grassland ecosystem, even if it is a smaller human-made version like a lawn or ditch. This video introduces a significant biome that is often converted to agricultural use: temperate grasslands.
Here is a quick look at prairie just south of Corvallis in the Willamette Valley.
Temperate grassland areas with large-flowered plants interspersed with the grasses are often called meadows.
We will have more on the term “monocot” (grasses) and large-flowered “dicots” in Guide 4A.
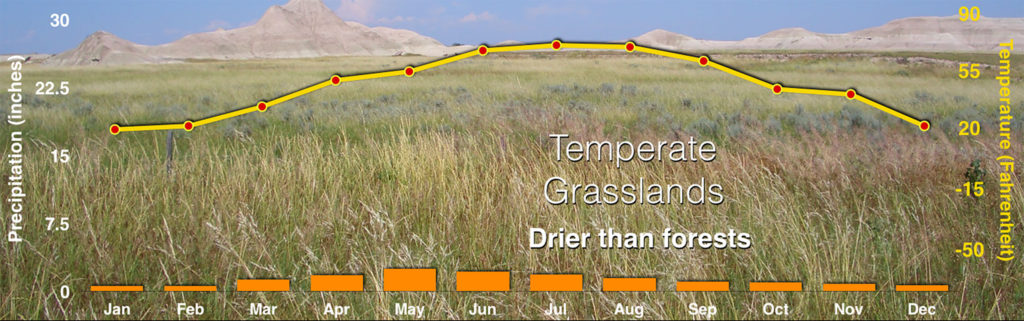
Temperate, meaning “not too hot or too cold; not too hot or too dry,” grasslands are typically found in climate conditions somewhere between a desert and a forest. Much of the swaths of temperate grasslands on this general biomes map have been converted to agricultural use.
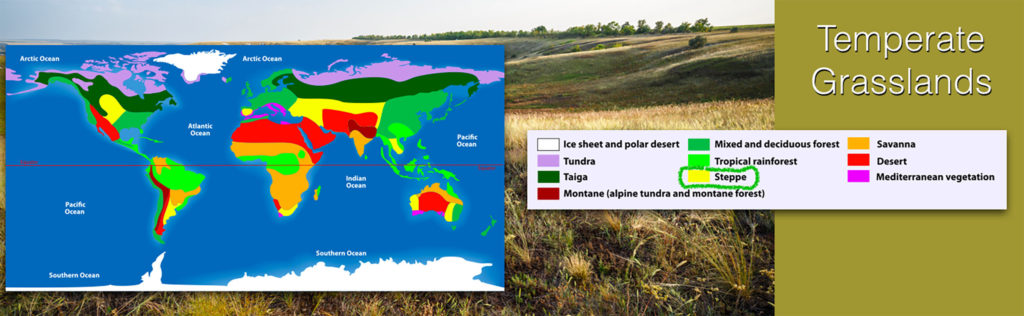
There is enough moisture for grasses, but it is too dry to sustain many, if any, ____.
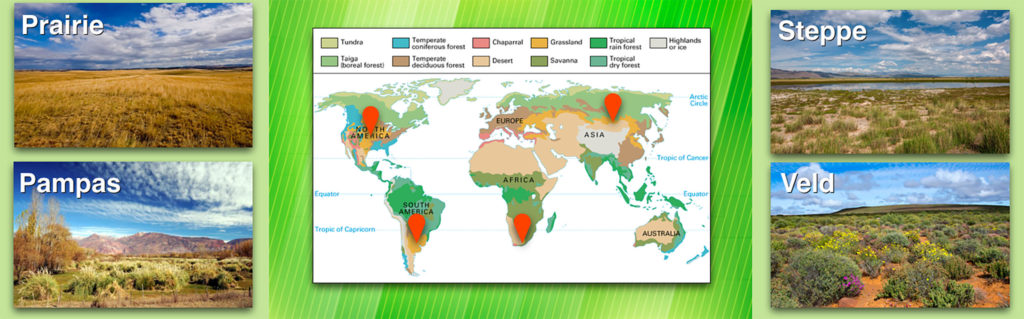
Temperate grasslands have many names, including:
North America: ____
Asia: ____ (these are the largest temperate grasslands, so this is how much of the world refers to these ecosystems)
South Africa: ____
South America: ____
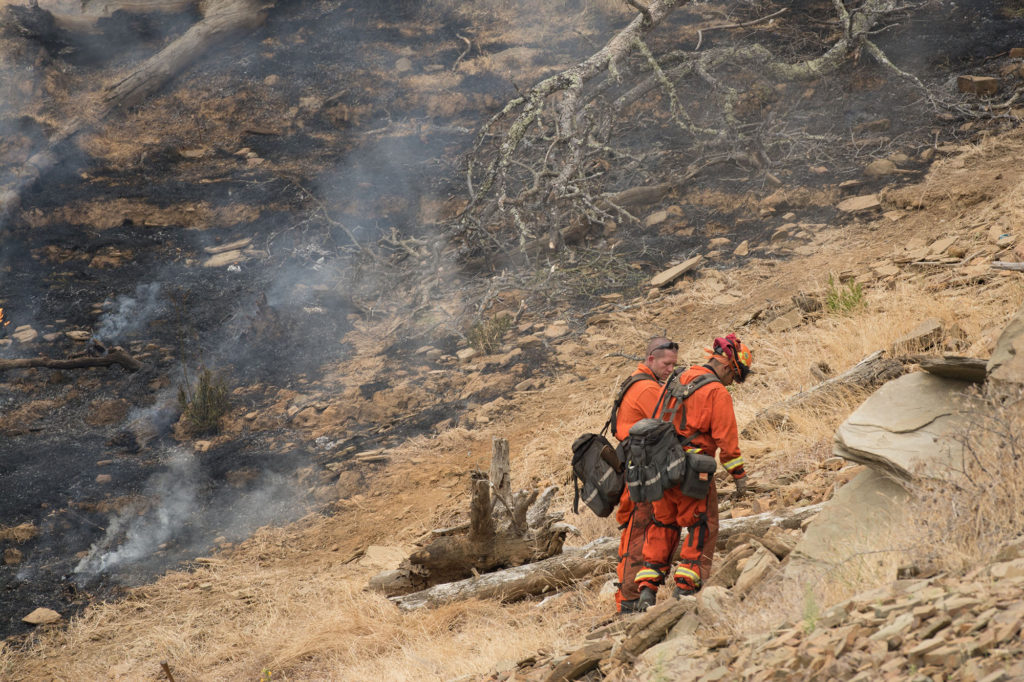

Grasslands are susceptible to fires. Dry conditions combined with the fuel of dry leaves can lead to fast-burning fires.
There are ecosystem benefits associated with grassland and forest fires. Fires kill grass pests and also speed up recycling of nutrients back to producers.
The next section describes the process of making field notes and introduces tropical grasslands.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- Describe what a pattern is and provide examples of patterns in nature?
- Identify different forms of population data including a population size chart, carrying capacity, and population distribution?
- Provide the names, locations, and characteristics of temperate grasslands?



