
Symbiosis Close Associations Over Time


Symbiosis Objectives:
- Define symbiosis, including the characteristics of mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism.
- Provide examples of organisms in mutualistic, parasitic, and commensalistic relationships.
- Describe different forms of endosymbiosis including how organisms are impacted.
The next section introduces symbiosis, a close association between organisms of different species. These close relationships can have impacts that are positive, negative, and even neutral.
Symbiosis (++, +-, +0)
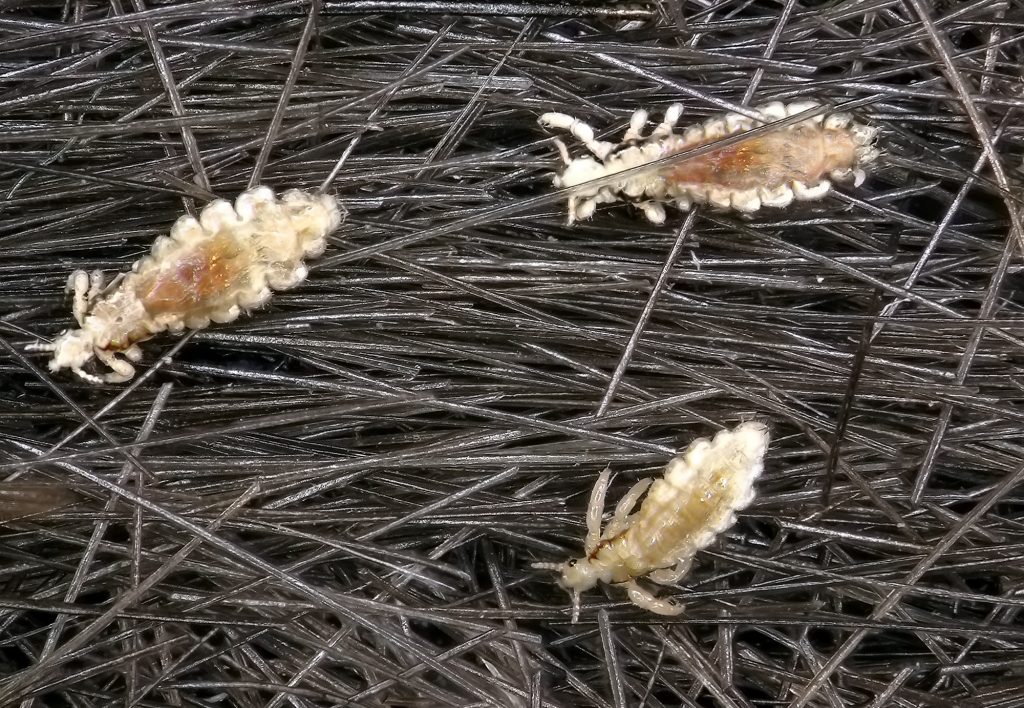

We use the word “symbiosis” in everyday language to mean getting along together, like having a symbiotic relationship with a roommate. In biology, symbiosis means living closely together, sometimes for long periods of time, and the outcome is not necessarily beneficial for all participants.
Three Types of Symbiosis

Mutualism
Both species in the interaction benefit. Lichens are typically an example of mutualism: the algae or cyanobacteria have a place to live and the fungus receives nutrients.

Parasitism
One species benefits, the other is harmed but typically not killed. Lice get a blood meal and it typically does not kill the host.

Commensalism
One species benefits, the other does not appear to be impacted. Moss growing on tree limbs get access to sunlight, but the trees can grow and reproduce as well without them.
There is a lot going on in this video: the hermit crab is using a sponge instead of a snail shell for protection. The sponge may or may not be impacted by this arrangement. If its not impacted, but the hermit crab is benefiting, this is an example of ______. The algae growing on the sponge is getting more surface area for growth and possibly additional nutrients, but the sponge it is growing on is not getting as much food into its pores. This example of one species benefiting and the other being harmed is _____.
Many clownfish species form relationships with anemone. The clownfish benefit as they are protected from potential predators by the anemone’s stinging tentacles. The anemone does not appear to be impacted. This is an example of _____.
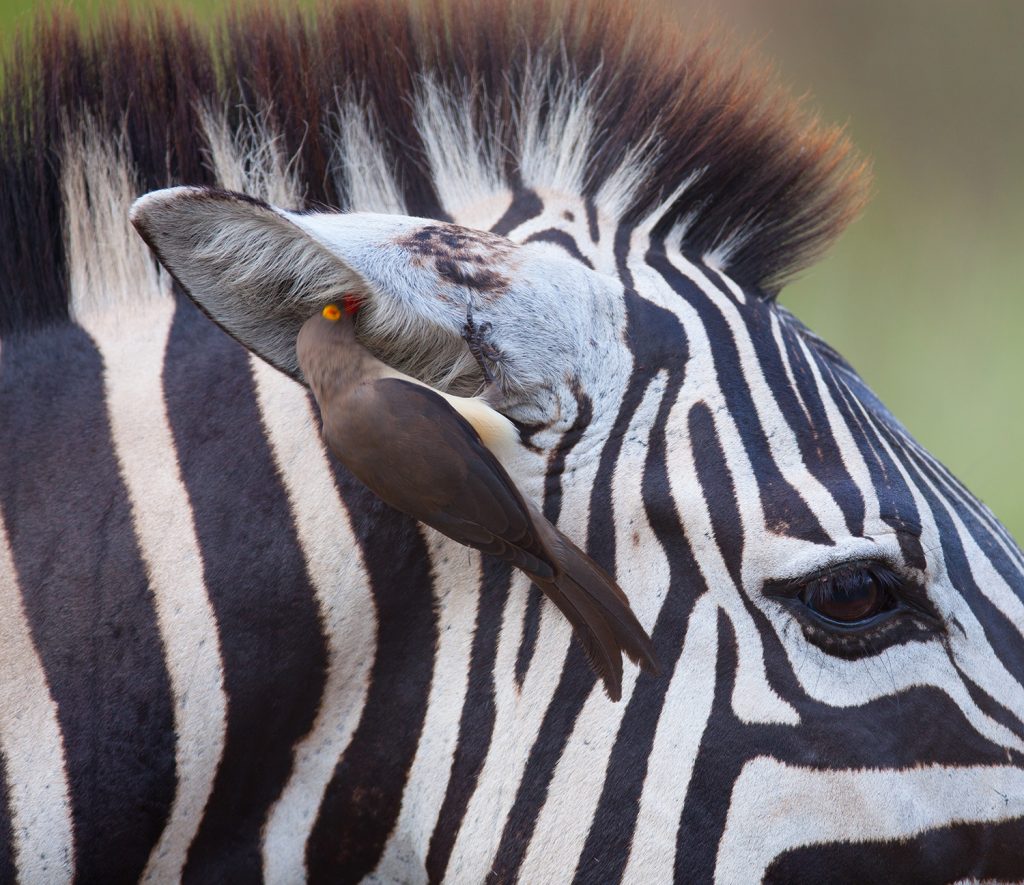
Some animals get a significant portion of their nutrients by cleaning other species Oxpeckers are African songbirds that eat ticks, blowfly larvae and other parasites off the skin of large mammmals. The oxpecker bird gets food and the mammal has fewer parasites. This is an example of _____.








Cleaner Shrimp, made popular by the movie “Finding Nemo,” get their food from a number of sources, including cleaning fish, removing dead scales, dirt, and parasites.
This cleaner shrimp tries to clean one of the clownfish. The fish could damage the shrimp, but does not appear to be alarmed.
These cleaner shrimp have learned to take food form the hand and readily clean under fingernails.
Endosymbiosis

Endosymbiosis is a more specific form of symbiosis when one species lives inside of another for a period of time. The anemone we can find in out coastal tide pools have green bodies because there are green algae living inside of them. The algae get a place to live and the anemone get some of the photosynthetic product. This is an example of mutualistic endosymbiosis.
Mycorrhizae (fungus living within plant roots) and Rhizobium (bacteria living within legume roots) are also examples of endosymbiosis.

Mycorrhizae
The relationship between the fungus and the plant root it live inside is most likely _____ endosymbiosis.

Rhizobium
The relationship between the bacteria and the plant root it lives inside of is most likely _____ endosymbiosis.
Many endosymbiotic species interactions can be observed in the Willamette Valley.
We have already met the lichens.
Summarize in your own words what a lichen community is, including the types of organisms and how they relate to one another.

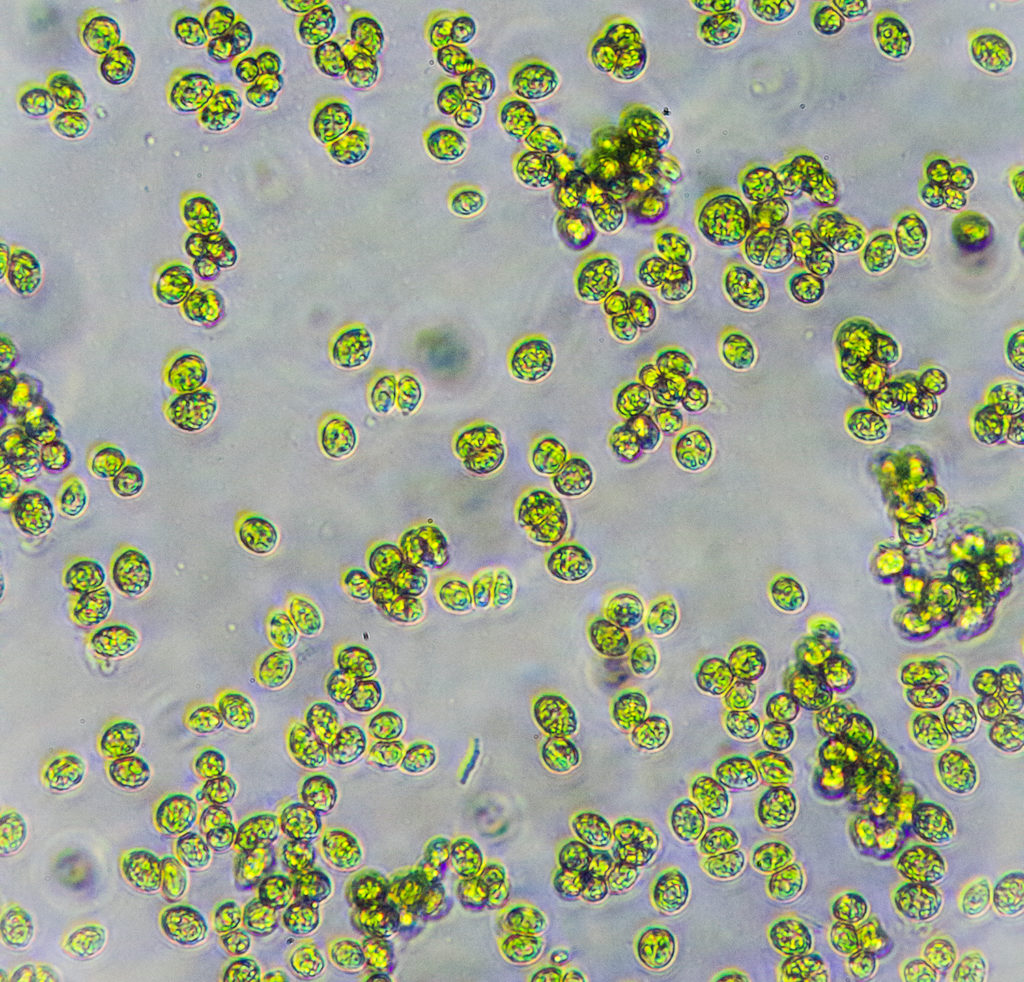
Anabaena blue-green cyanobacteria can also live inside of aquatic Azolla ferns. The bacteria are protected; the plant gets nutrients in return.
Azolla fern floats on the surface of freshwater ponds. The next two videos demonstrate the endosymbionts within these plants.
Azolla fern up close, with a few other organisms along for the ride in this pond sample.
Under the microscope, the endosymbionts become visible.
The next section introduces interactions within an oak community.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- Define symbiosis, including the characteristics of mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism?
- Provide examples of organisms in mutualistic, parasitic, and commensalistic relationships?
- Describe different forms of endosymbiosis including how organisms are impacted?





