
Wetlands Part Aquatic; Part Terrestrial


Wetlands Objectives
- Provide examples of different types of wetlands.
- Describe various wetland functions including why it is challenging to rebuild a wetland.
- List characteristics of amphibian species including the frog life cycle.
Wetlands are terrestrial habitats that are sometimes wet and sometimes dry.
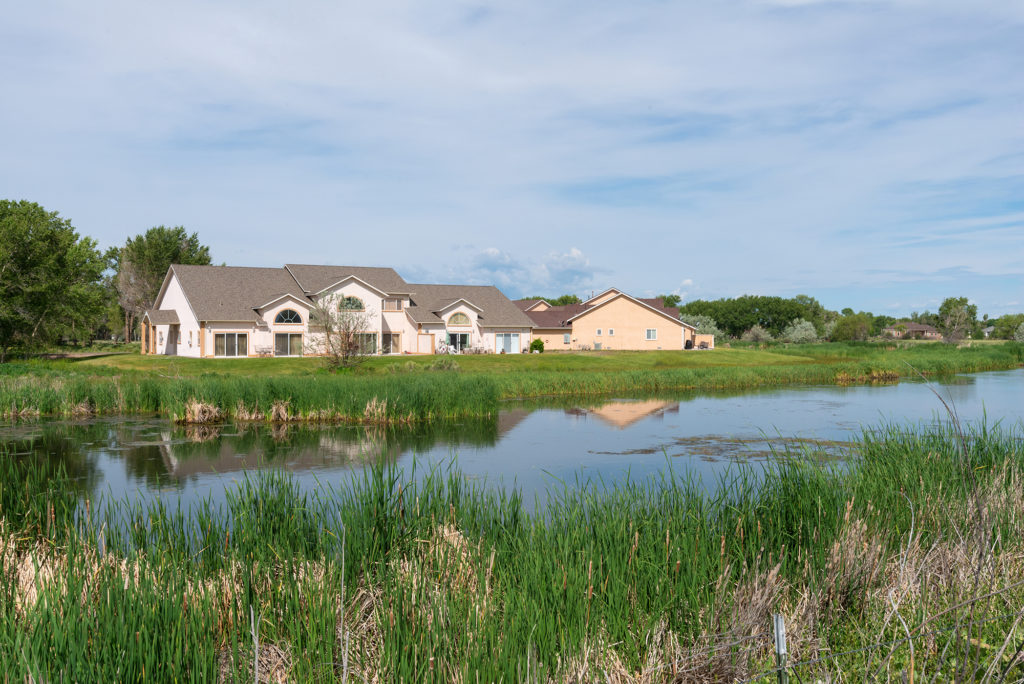

Wetlands can appear very different depending on the time of year. Identification is critical, particularly when deciding whether to develop land for human use.
Plant and soil specimens are used to recreate the characteristics of the habitat over time. There are dozens of different wetland types based on soil profiles.
Here are a few examples of the many types of wetlands.
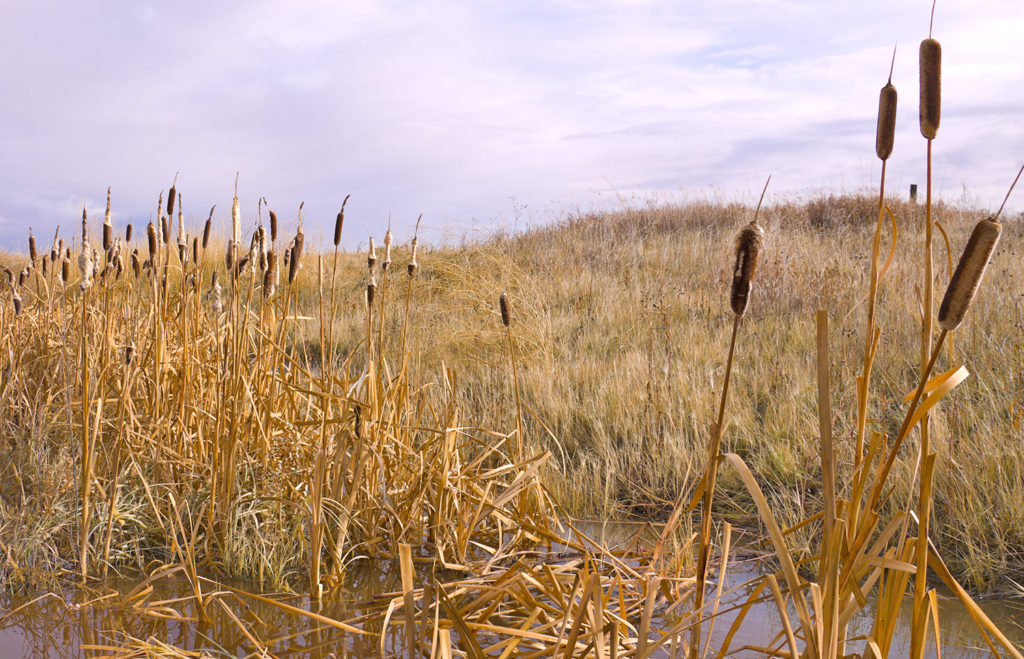

Wet Prairie
Grasses and wildflowers with few, if any, trees. Wet prairies are found in the Willamette Valley of Oregon.
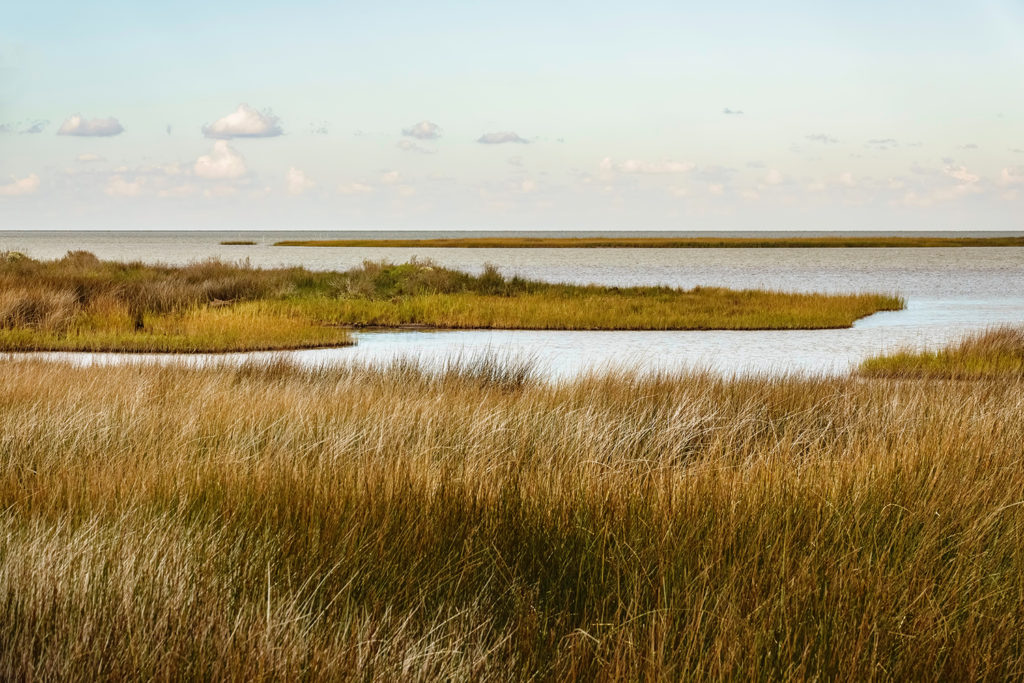

Marsh
Often coastal with an influx of salt water mixing with freshwater. Can be large and are typically dominated by grasses.
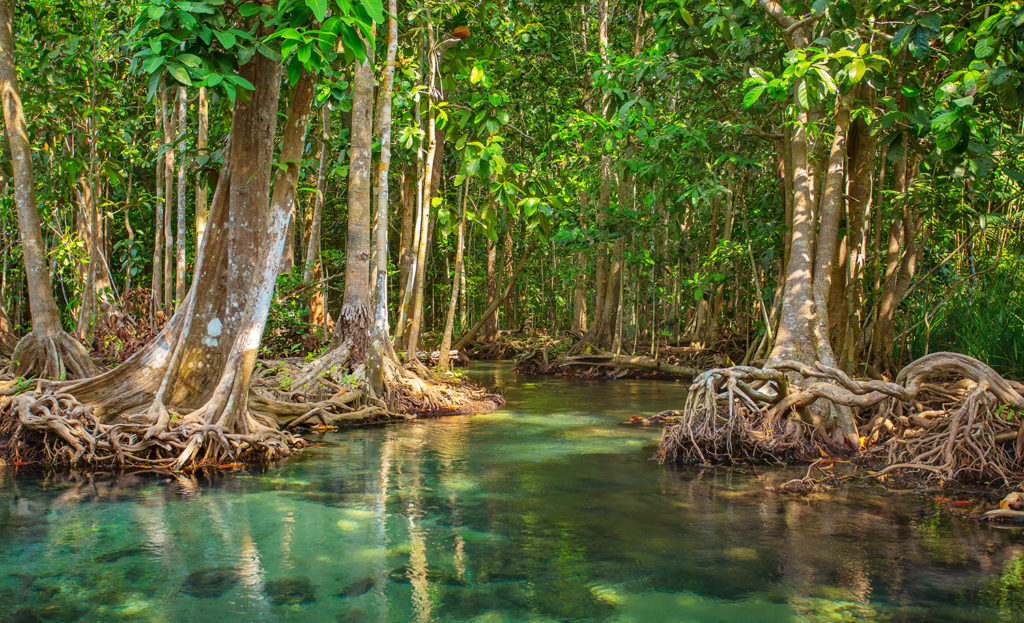

Swamp
Can include tree species that survive water-logged soils. Many are coastal.
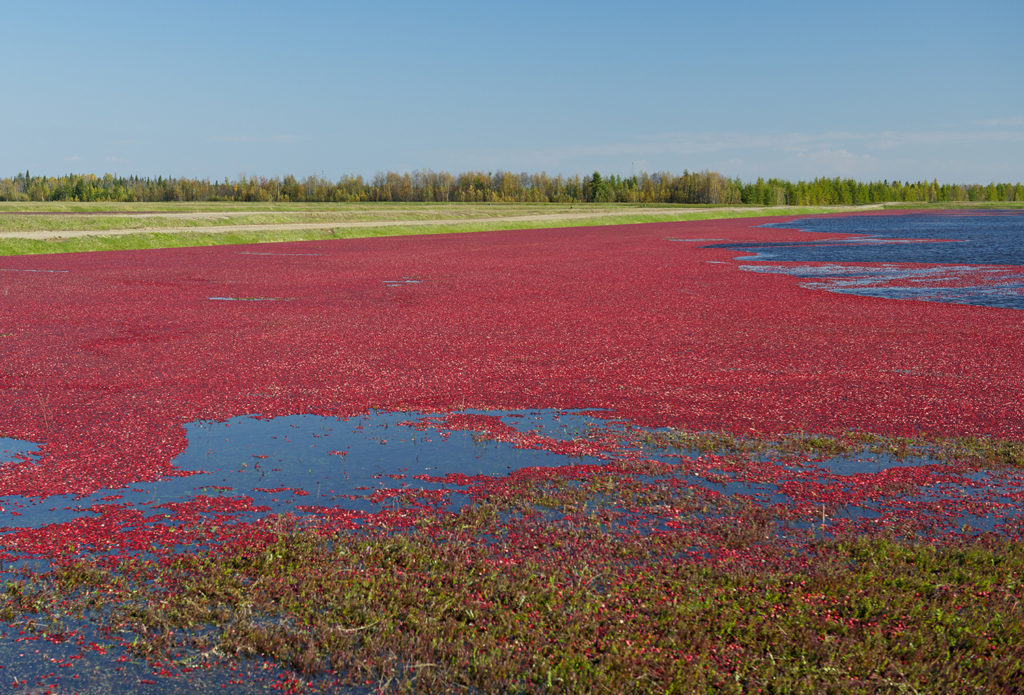

Bog
Can include peat moss and often are found in colder climates. Source of cranberries.

Oregon has many types of wetlands. Some of the coastal marshes have been converted into cranberry fields.
Wetlands have high productivity that supports herbivores and carnivores like herons.
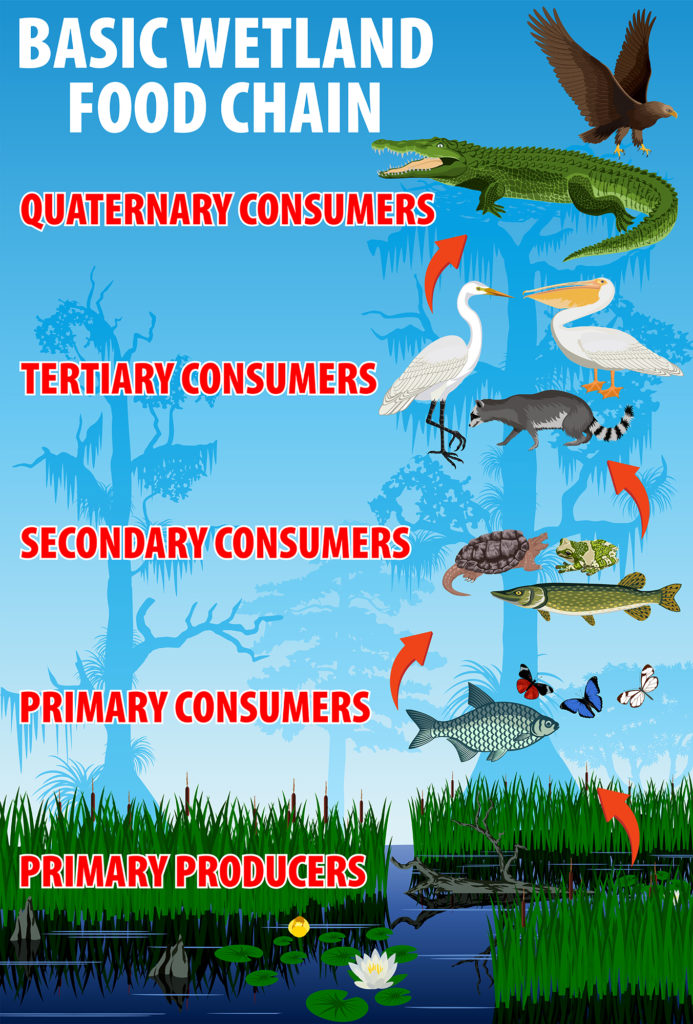
Wetlands have the three ingredients necessary for high productivity (photosynthesis): water, light, and nutrients.
Producers are abundant and include the macroscopic submerged plants as well as microscopic algae and bacteria.
Wetland plants are similar to the plants found along the shallow shores of lakes.
This video was taken at the Oregon Gardens.

The complexity of wetland food webs makes them challenging to manage or rebuild. Digging new holes that fill temporarily with water does not necessarily produce the soil profile necessary to support wetland producers and a diverse community.
Until recent decades, wetlands were often seen as useless land. The majority of wetlands around populated areas were filled in with dirt before their important functions became evident.
This video lists a few of the many important wetland functions.
Important Wetland Functions

Remove Carbon Dioxide from the Atmosphere
Photosynthetic organisms extract carbon dioxide from the air and water. The abundance of producers in wetlands adds up to a significant impact on atmospheric gases that retain heat (“greenhouse effect”).

Recharge Groundwater
We extract water from the ground (“well-water”) to irrigate crops, support industry, and support remote residences. New water percolates through the soil from the surface, and a disproportionately high amount of this groundwater recharge happens through wetland soils.
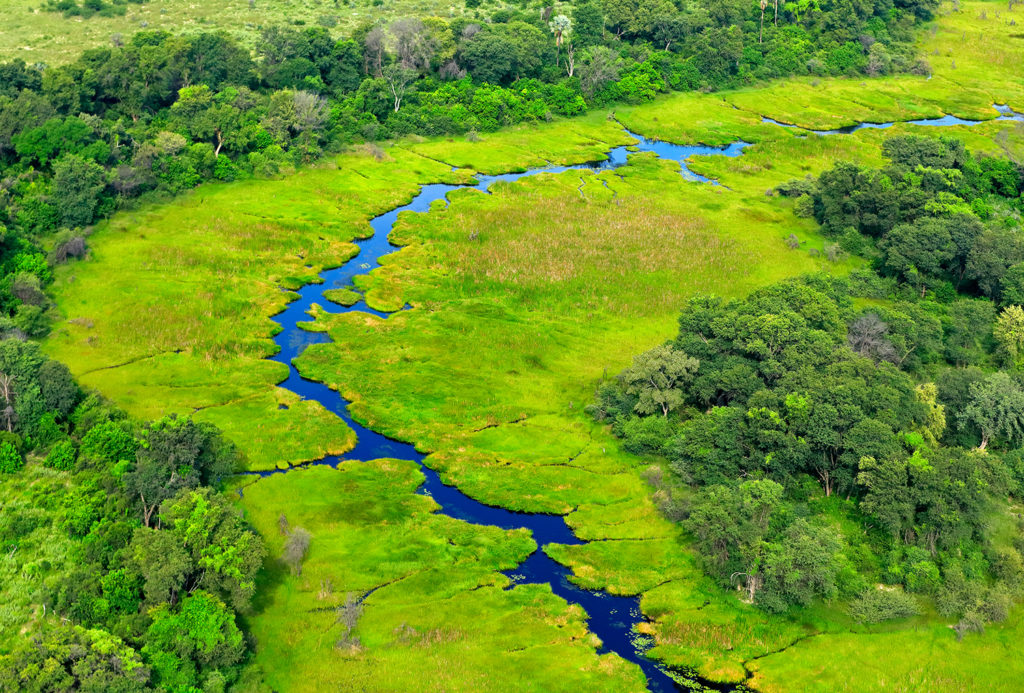

Control Flood Waters
Rivers are often bordered by wetlands. During flood events, the wetlands can absorb much of the extra water. When wetlands are removed around rivers, flooding extends further away from the river banks, causing more extensive damage.

Filter Pollutants
Wetlands filter pollutants from the rivers they surround. Slower moving water in the wetland areas causes pollutants to settle into the soils. Removal of wetlands around the Mississippi River has led to increased release of pollutants into the Gulf of Mexico.
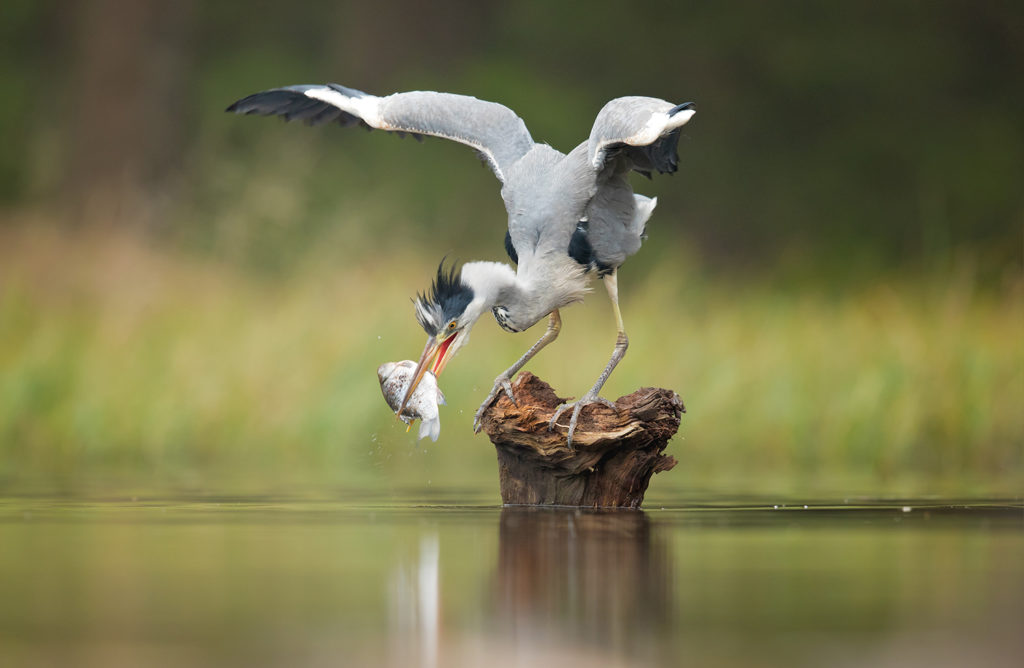

Habitat
The high productivity of wetlands makes them ideal habitats for supporting higher tropic (feeding) levels. This includes migratory animals like ocean-going salmon, geese, and many other water birds.
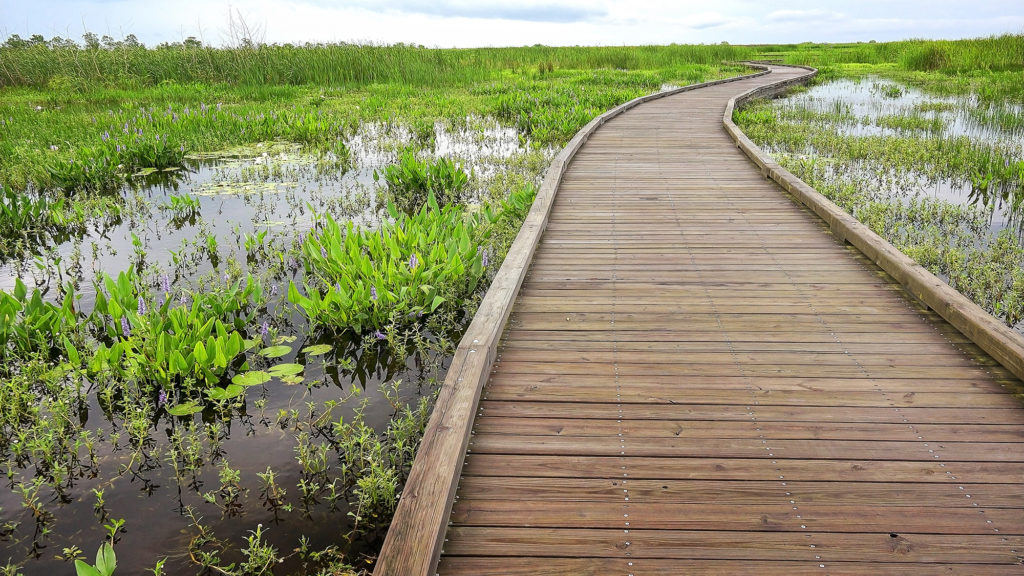

Recently wetlands have become destinations for outdoor excursions that highlight ecosystem diversity. Since rebuilding a complex wetland food web is incredibly difficult, working around wetlands is sometimes the solution.
Amphibians
When you walk along a wetland path or on the boardwalk, you can often hear the “plunk” sound of frogs and newts jumping into the water. This video introduces the amphibians.
Frogs and toads are the most common amphibians, but their names can be misleading.
Terminology is often constructed for ease of communication, but misconceptions can result.
One of the first biology lessons in elementary grades is on the frog life cycle.
Fill in a few gaps and learn why this is such a popular topic.
This summer we had over a dozen Pacific Tree Frogs in our garden. These native species can live in moist microhabitats.
Now that you have completed this section, list five characteristics of amphibians like this frog.
This is the end of Guide 7B. Please proceed to the product page.

Check your knowledge. Can you:
- provide examples of different types of wetlands?
- describe various wetland functions including why it is challenging to rebuild a wetland?
- list characteristics of amphibian species including the frog life cycle?



